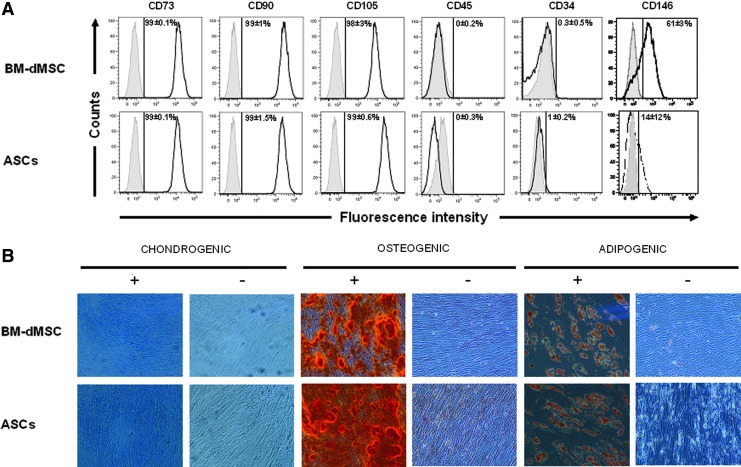
FIG. 1.
Characterization of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC). (A) Phenotype of MSC. MSC derived from bone marrow (BM-dMSC) (passage 2) and adipose tissue (ASC) (passage 3) were analyzed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting after staining with conjugated monoclonal antibodies against surface markers (black line) or IgG control isotypes (gray line). Results were representative of three independent experiments. The mean percentage of fluorescence above the threshold for isotype controls is indicated. (B) Differentiation potential of MSC for mesodermic lineage: MSC were cultured in a medium with (+) or without (−) differentiation cocktails for 3 weeks. Chondrogenic, osteogenic, and adipogenic differentiation were observed, respectively by coloration with Alcian Blue, which detects proteoglycans of chondroblasts, Alizarin Red, which detects calcium mineralization of osteoblasts and Oil red O, which detects lipid vesicles in adipocytes. Results depicted the differentiation of MSC derived from the bone marrow (BM-dMSC) or ASC from one donor out of three. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tea