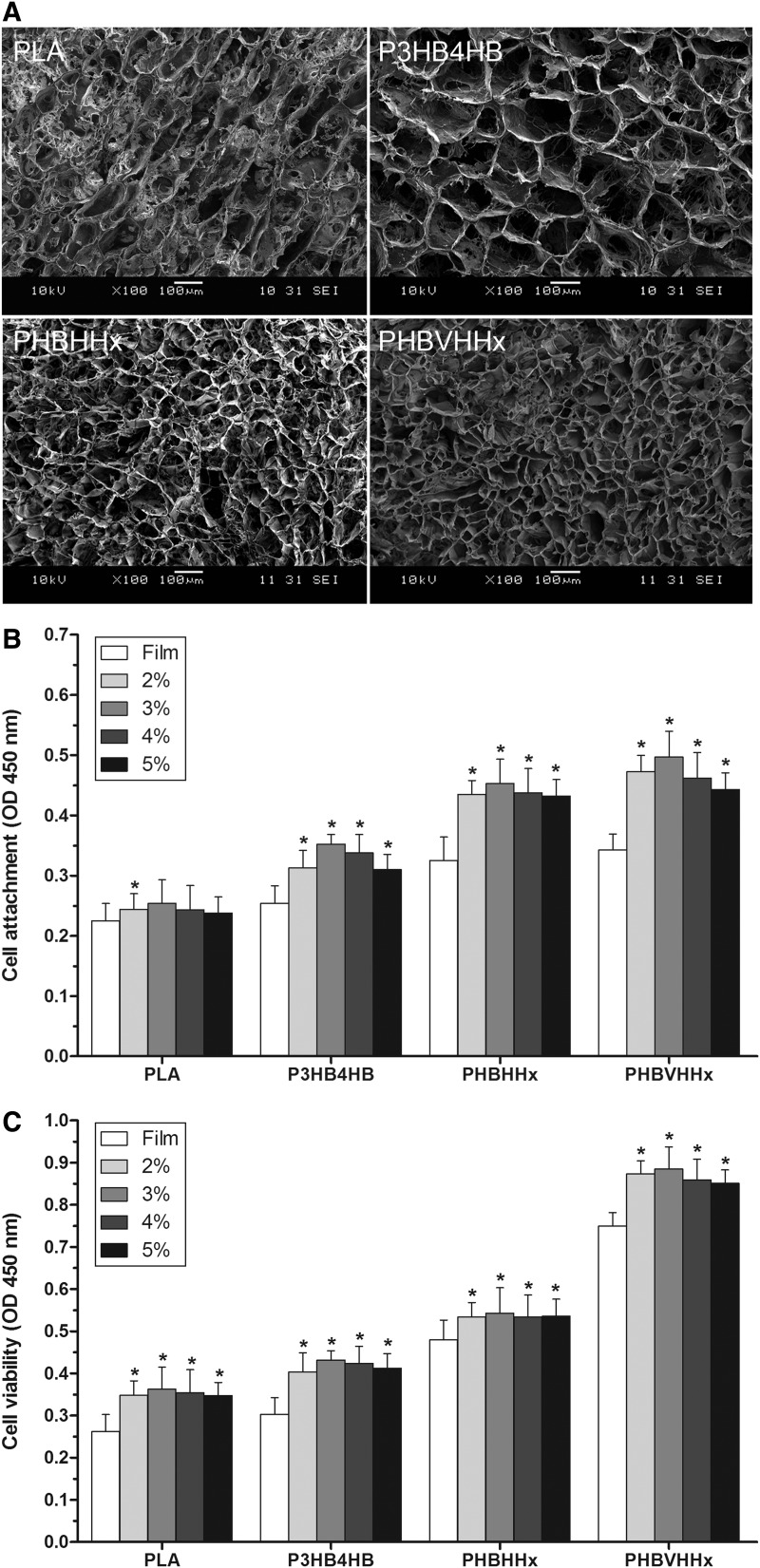
FIG. 1.
Examination of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly (WJ-MSCs) loaded into polymer scaffolds. (A) Scaffolds were prepared from different polymers and examined by scanning electron microscopy. Different polymer scaffolds displayed the different pore sizes. (B) Analysis of attachment of WJ-MSCs loaded into polymer scaffolds. The different polymer scaffolds were prepared at concentrations of 2%, 3%, 4%, and 5%, and the different films at 2%. Cell attachment on the different films and scaffolds was studied using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay after WJ-MSCs were incubated for 4 h. Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) (PHBVHHx) scaffolds exhibited the highest cell attachment compared with the other commonly used polymers (n=6). *p<0.01 versus respective film. (C) Analysis of viability of WJ-MSCs loaded into polymer scaffolds. Cell viability on the different films and scaffolds was studied using CCK-8 assay after WJ-MSCs were incubated for 72 h. PHBVHHx scaffolds showed much higher cell viability than the other commonly used polymers (n=6). *p<0.01 versus respective film.