Figure 11.
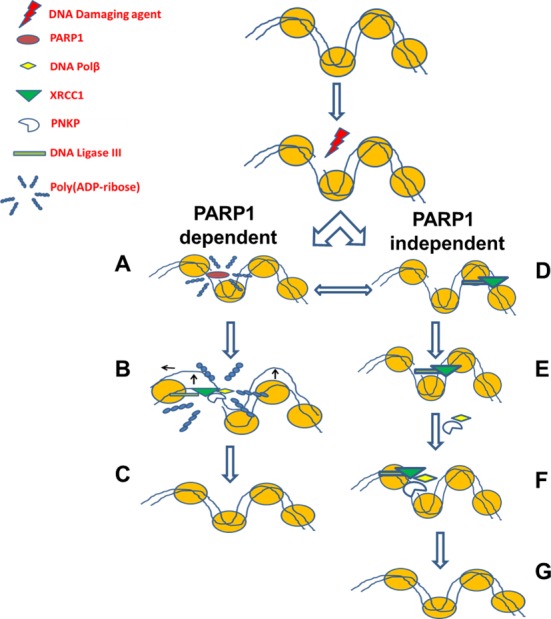
Two pathways exist for the short patch repair of SSBs. In the canonical pathway (PARP1 dependent) (A) PARP1 senses DNA damage and rapidly catalyzes the formation of PAR residues that allow for (B) chromatin expansion which in turn facilitates (C) the recruitment of downstream repair proteins. In the second pathway (PARP1 independent) (D) XRCC1–LIG3 complex continuously scans the DNA, upon sensing an interruption (via LIG3), (E) the complex is capable of causing a localized nucleosomal disruption (dependent on LIG3) (42), and the scaffold XRCC1 is capable of (F) loading downstream repair factors, PNKP and Polβ, and then repair continues as previously described (G).
