Figure 1.
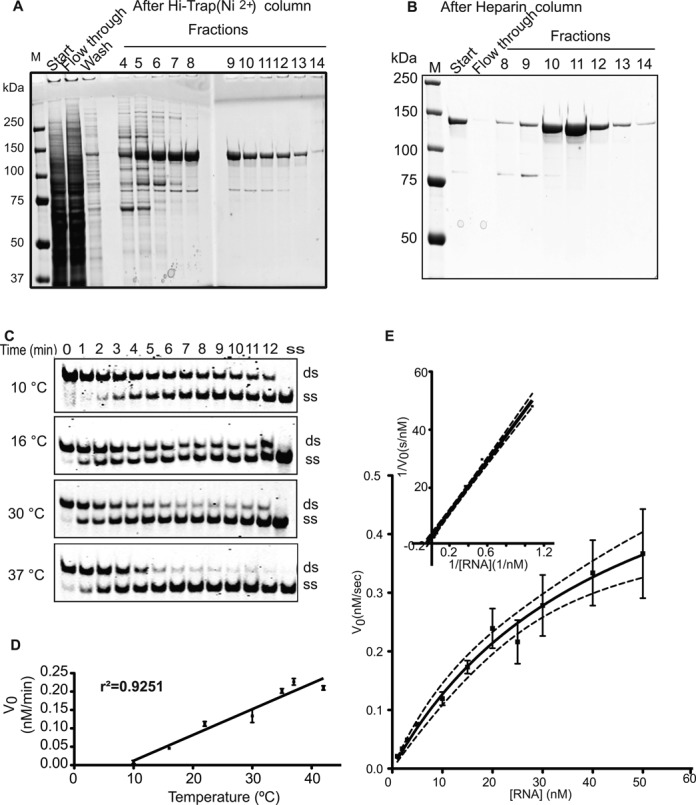
Recombinant RHA is a highly active helicase. (A) Eluted RHA fractions from the Hi-Trap nickel column stained with Coomassie Blue. (B) Heparin column-purified RHA stained with Coomassie. (C) One nanomolar RHA separated 1-nM dsRNA in a temperature- and time-dependent fashion to single strands. (D) The initial rates of the reactions were plotted against the temperatures. The linear correlation coefficient of this plot was found as r2 = 0.9251. All reactions were carried out three times. (E) Michaelis–Menten kinetics graph, the x-axis represents the substrate (dsRNA) concentration in nM, and the y-axis represents the initial velocity at the corresponding substrate concentration. The kinetics experiments were repeated three times and differences among individual results represented in the error bars. Inset of (E): Lineweaver–Burk transformation plot of the RHA helicase enzyme reaction.
