Figure 1.
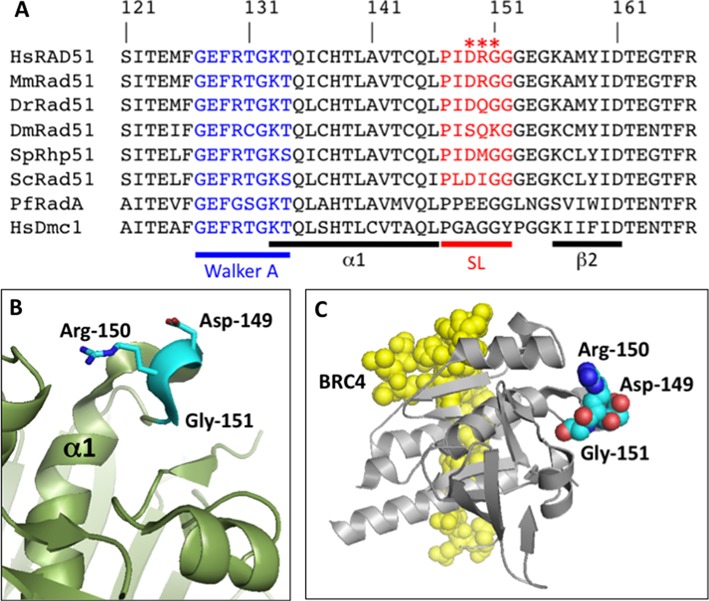
Sequence alignment and structure of the Schellman loop region of human RAD51 protein. (A) BLAST alignments of the Schellman loop region of Homo sapiens RAD51 protein (HsRAD51) to orthologs from Mus musculus (MmRad51), Danio rerio (DrRad51), Drosophila melanogaster (DmRad51), Schizosaccharomyces pombe (SpRhp51), Saccharomyces cervisiae (ScRad51) and Pyrococcus furiosus (PfRadA), and to Homo sapiens DMC1 protein (HsDMC1). The position of the conserved Schellman loop (SL) motif is indicated in red. Residues 149–151 in human RAD51, which are mutated in tumor-associated variants D149N, R150Q and G151D, are marked by red asterisks. The position of the Walker A motif is indicated in blue. Sequences corresponding to α-helix 1 (α1) and β-strand 2 (β2) are indicated by the black bars. (B) Structure of the Schellman loop region of human RAD51. Residues Asp-149, Arg-150 and Gly-151, which are mutated in tumor-derived variants, are highlighted in cyan. (C) Structure of the human RAD51–BRC4 complex, showing the relative positions of the BRC4 peptide (yellow, space-filling) and the RAD51 core domain (silver, cartoon) with Asp-149, Arg-150 and Gly-151 residues highlighted (colored by atom, space-filling). Structures in (B) and (C) were rendered from PDB ID: 1N0W.
