Figure 3.
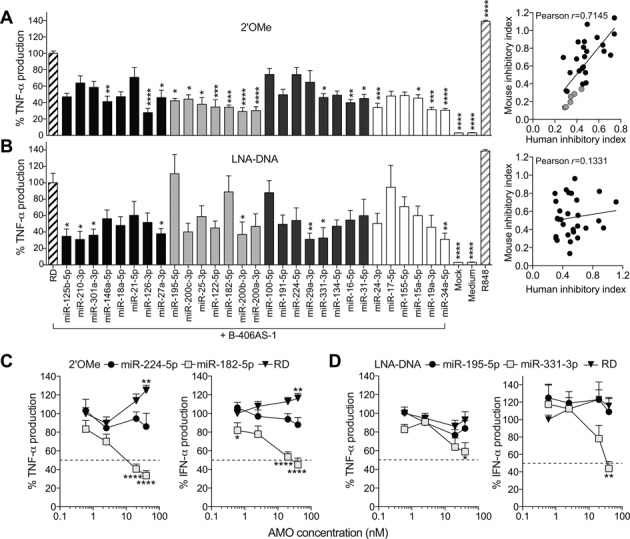
Sequence-dependent inhibition of RNA sensing by 2′OMe AMOs is conserved in human PBMCs. Human PBMCs pre-treated with 40 nM of the indicated 2′OMe AMO (A) or LNA/DNA AMO (B) for 45 min were stimulated overnight with 180 nM of B-406AS-1. TNF-α levels were measured in supernatants by ELISA. Correlation of relative TNF-α production to RD control condition (i.e. inhibitory index) in both human PBMCs and mouse BMMs is shown for each AMO chemistry (right panels). 2′OMe AMOs of ‘Class 2’ are shown in grey. Correlation for 2′OMe AMOs was highly significant (P < 0.0001). (C and D) Human PBMCs were pre-treated for 45 min with the indicated dose of AMO or RD, and stimulated overnight with 180 nM of B-406AS-1. (C and D) TNF-α and IFN-α levels were measured in supernatants by ELISA. (A–D) The data are averaged from a minimum of three independent experiments in different blood donors, in biological triplicate. Percentages of cytokine production compared to the RD+B-406AS-1 condition (A and B) or the 0.6 nM RD+B-406AS-1 condition (C and D) are given. Ordinary one-way (A and B) or two-way (C and D) ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple comparison tests to the RD+B-406AS-1 (A and B), the miR-224-5p+B-406AS-1 (C) or the miR-195-5p+B-406AS-1 (D) conditions are shown. (A–D) Unless otherwise indicated, differences were not significant. SEM is shown.
