Figure 1.
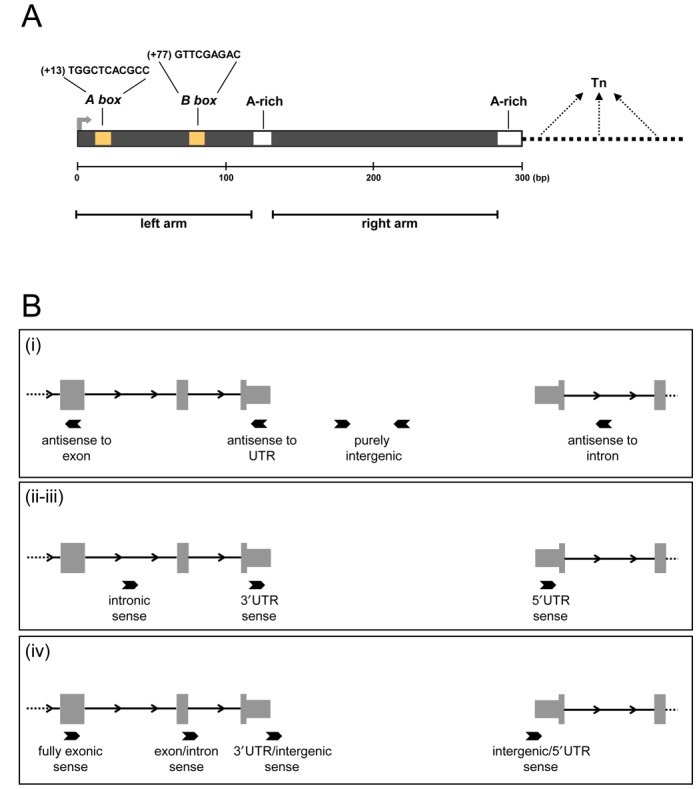
Architecture of Alu elements considered as RNA polymerase III transcription units. (A) Schematic representation of a typical Alu element, ∼300 bp in length (indicated by graduated bar). Alu transcription by RNA polymerase III requires A box and B box internal promoter elements (orange bars) (6), which form together the binding site for TFIIIC. The consensus sequences for Alu A and B boxes are reported above the scheme. While the Alu B box sequence perfectly matches the canonical B box sequence found in tRNA genes, the sequence of Alu A box slightly diverges from canonical A box sequence (TRGYnnAnnnG; (5)). Transcription is thought to start at the first Alu nt (G) (3,4). The A box starts at position +13, the B box 53 bp downstream, at position +77. The left and right arms of the Alu, each being ancestrally derived from 7SL RNA, are separated from each other by an intermediate A-rich region, starting 35 bp downstream of the B box, whose consensus sequence is A5TACA6. Another A-rich tract is located 3′ to the right arm, at the end of the Alu body, starting at ∼150 bp downstream of the middle A-rich region. Transcription termination by RNA polymerase III is expected to mainly occur at the first encountered termination signal (Tn) downstream of the 3′ terminal A-rich tract. Such a signal, either a run of at least four Ts or a T-rich non-canonical terminator (25), may be located at varying distances from the end of the Alu body, thus allowing for the generation of Alu primary transcripts carrying 3′ trailers of different lengths and sequences. (B) Possible localizations of Alu elements with respect to other transcription units: (i) intergenic/antisense, comprising purely intergenic Alus as well as Alus which are not included in longer transcription units on the same strand, but overlap in antisense orientation to transcription units located on the opposite strand; (ii and iii) gene-hosted, comprising Alus fully contained within introns or UTRs of protein-coding or lincRNA genes in a sense orientation; (iv) all other cases, including Alu RNAs fully or partially mapping to exons, or partially mapping to UTRs, in a sense orientation.
