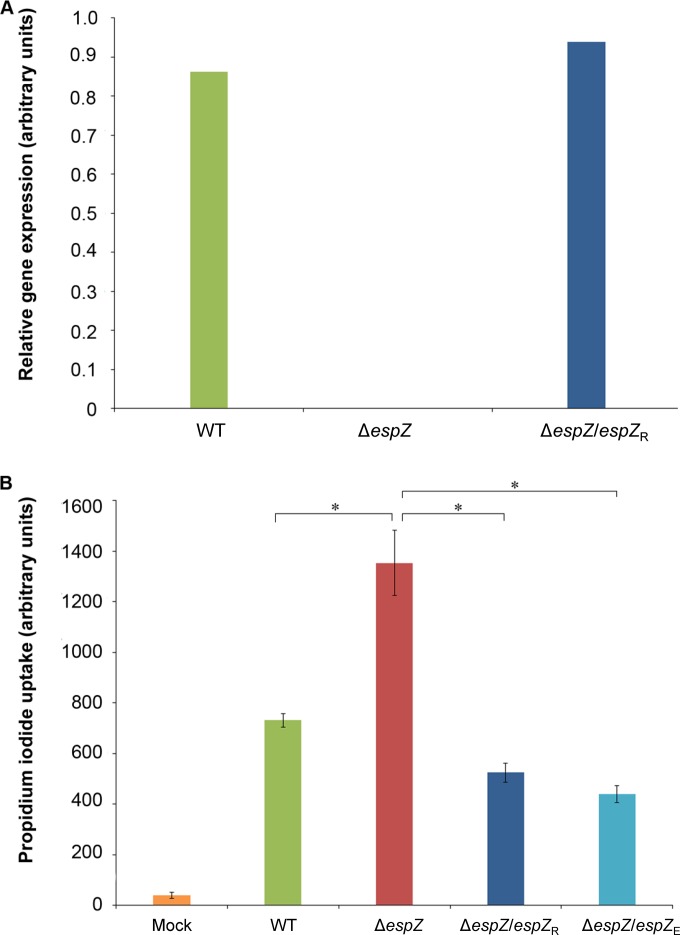
FIG 1.
Both the REPEC and EPEC EspZ proteins protect epithelial cells from REPEC-induced death. (A) Reverse transcription analyses demonstrating comparable espZ expression levels in the REPEC parental (WT) strain and the cis-complemented REPEC ΔespZ strains. Relative gene expression levels are shown and were derived via densitometric analyses of the linear phase of espZ amplicon accumulation. Data are normalized to the expression levels of the E. coli genes escI and groE. (B) PI uptake cell death assay using C2BBE host cells infected with the parent REPEC strain (green bar), the ΔespZ mutant (red bar), and the ΔespZ mutant cis-complemented with espZ from REPEC (ΔespZ/espZR) (dark blue bar) or from EPEC (espZ/espZE) (light blue bar) for 4.5 h. Data are presented as average PI uptake rates ± standard errors of the means for eight technical replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences (P ≤ 0.05).