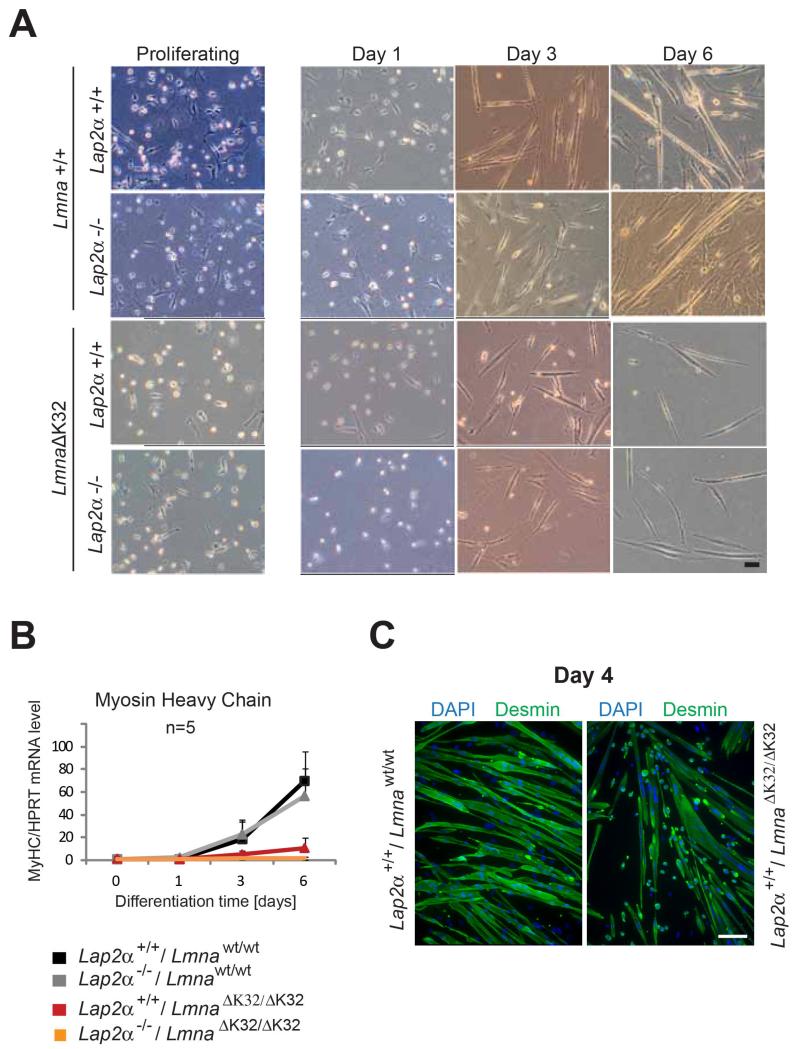
Fig. 7. Primary LmnaΔK32/ΔK32 myoblasts exhibit delayed and insufficient in vitro differentiation irrespective of presence or absence of LAP2α.
Primary murine myoblasts were isolated from newborn littermates and expanded and differentiated on collagen-coated dishes. At 1, 3 and 6 days after induction of differentiation, cultures were analyzed by various assays: (A) bright field images in the left column show proliferating myoblasts, those in other columns show myoblasts that have been plated at the same densities and induced to differentiate for 1, 3 and 6 days. A lag of LmnaΔK32/ΔK32 myoblast differentiation irrespective of LAP2α at day 3 and massive reduction of myotube formation at day 6 of in vitro muscle differentiation is detectable (bar = 100 μm). (B) Real time PCR analyses of myosin heavy chain (MyHC) normalized to endogenous levels of Hprt showing an absence of MyHC upregulation upon LmnaΔK32/ΔK32 myoblast differentiation. Means of 5 independent experiments are shown and only positive standard errors are shown as error bars. (C) Confocal immunofluorescence microscopic analyses of differentiating myoblasts at day 4 of differentiation stained with antibodies to desmin, showing impaired fusion of LmnaΔK32/ΔK32 myoblasts. DNA was stained with DAPI. Scale bar denotes 50 μm.