Figure 2. The SLX4-TRF2 Interaction Is Critical for Telomeric Localization of SLX4.
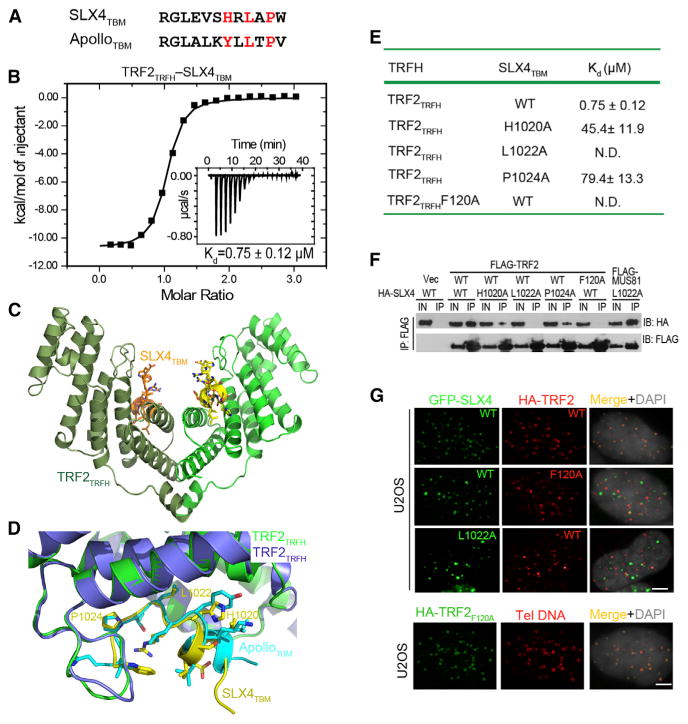
(A) Sequence comparison between SLX4TBM and ApolloTBM. Key residues that mediate the interaction with TRF2TRFH are highlighted in red.
(B) ITC measurement of the SLX4TBM-TRF2TRFH interaction. Inset shows the ITC titration.
(C) Overall structure of the SLX4TBM-TRF2TRFH complex. TRF2TRFH and SLX4TBM are colored in green and yellow, respectively, in one monomer, and dark green and orange, respectively, in the other.
(D) Superposition of the TBM peptide-binding sites in the SLX4TBM-TRF2TRFH and ApolloTBM-TRF2TRFH complexes. TRF2TRFH is colored in purple and green in the SLX4TBM-TRF2TRFH and ApolloTBM-TRF2TRFH complexes, respectively.
(E) Equilibrium dissociation constants (Kd) of WT and mutant SLX4TBM-TRF2TRFH interactions measured by ITC. N.D., not detectable.
(F) Co-IP of WT and mutant SLX4 and TRF2 in 293T cells. Lanes marked “IN” contain 5% of the input lysate used for IPs.
(G) Nuclear localization of WT and mutant SLX4 and TRF2. Telomeric DNA was detected by the Cy3-labeled (CCCTAA)3 PNA probe. Bar: 5 mm.
See also Figure S2.
