FIG 5.
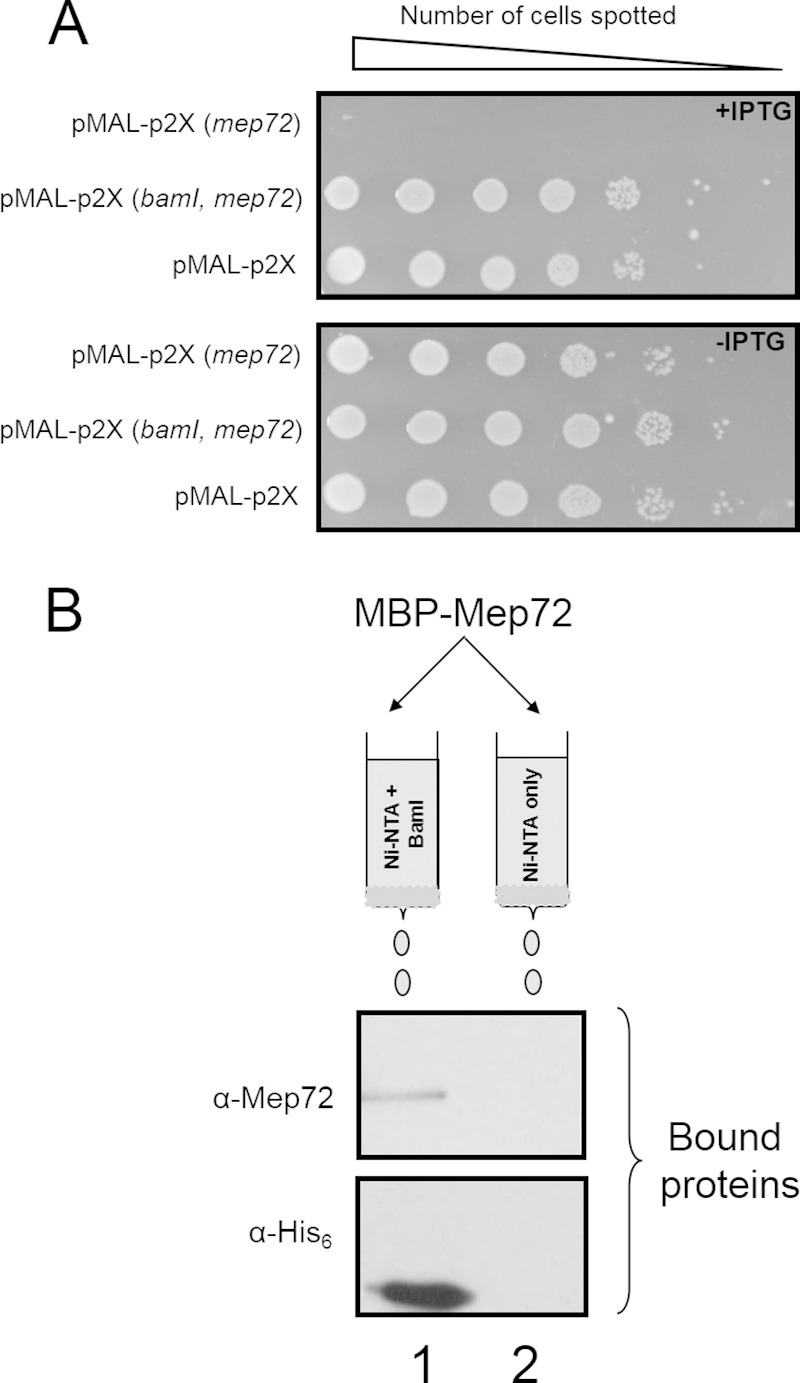
Ectopic expression of mep72 in E. coli is toxic but is counteracted by coexpression of mep72 with bamI. (A) Serial dilutions of E. coli carrying plasmid-encoded, IPTG-inducible MBP-Mep72 [pMAL-p2X(mep72)], BamI-MBP-Mep72 [pMAL-p2X(bamI, mep72)], and empty pMAL-p2X vector control (pMAL-p2X) were spotted onto LB-agar plates with and without IPTG. The spotted dilutions were allowed to grow for 24 h before being photographed. (B) Mep72 forms an isolable complex with BamI. His6-BamI was overexpressed in E. coli and refolded. The refolded protein was loaded onto an Ni-NTA affinity matrix. The matrix was washed to remove any unbound BamI. Following this washing, refolded MBP-Mep72 was passed over the matrix. Excess MBP-Mep72 was washed off, and the bound proteins were eluted in buffer containing 300 mM imidazole. The presence of BamI and Mep72 in the column loadings and eluates was determined by Western blotting using anti-His6 antibodies or anti-Mep72 antibodies, as indicated. As a control, we measured the binding of MBP-Mep72 to Ni-NTA beads that had not been pretreated with His6-BamI. Lane 1, eluate from column precharged with His6-BamI after adding 300 mM imidazole; lane 2, eluate from control column after adding 300 mM imidazole.
