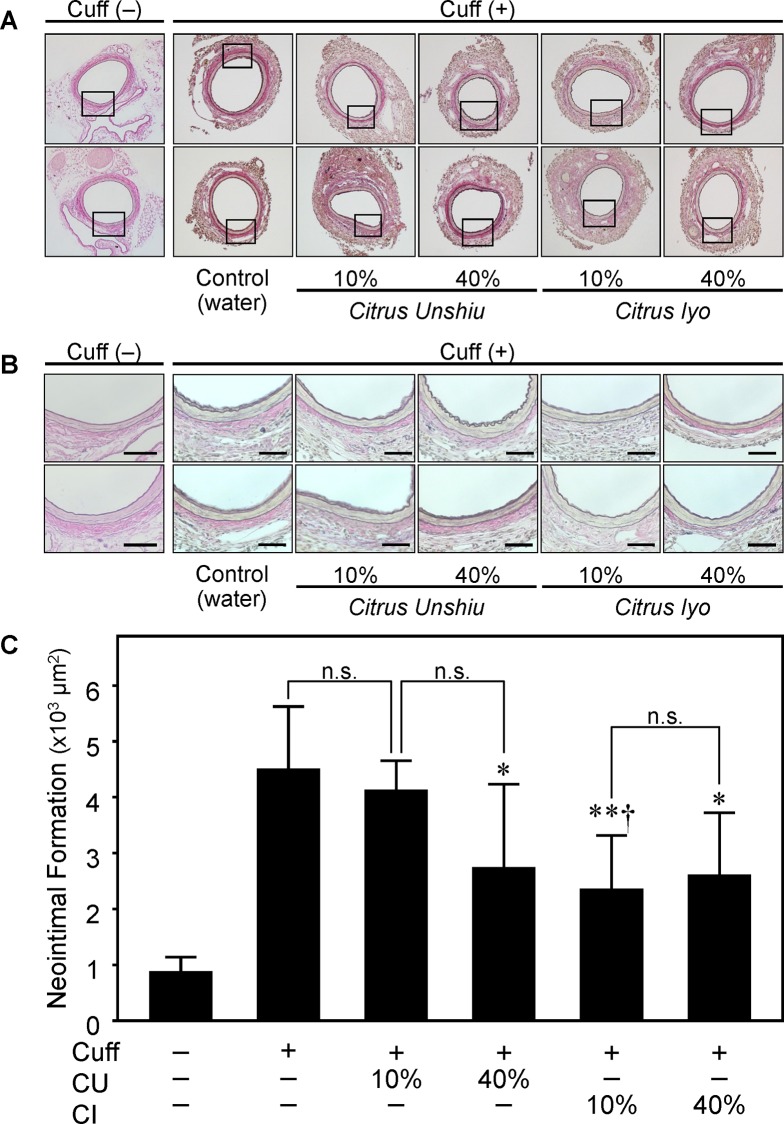
Fig 1. Effect of drinking citrus fruit juice on neointima formation.
Male C57BL6 mice were divided into five groups as follows: 1) Control (water) (C), 2) 10% Citrus unshiu (CU) juice (CU10), 3) 40% CU juice (CU40), 4) 10% Citrus iyo (CI) juice (CI10), and 5) 40% CI juice (CI40). After drinking them for 2 weeks from 8 weeks of age, cuff injury was induced by polyethylene cuff placement around the femoral artery. Samples were prepared from cuffed-femoral arteries of C57BL/6J mice as described in Methods. A, Representative photos of neointimal area in cross-sections of femoral artery with elastic van Gieson staining 14 days after cuff placement at 100x magnification. B, Higher magnified photos at 400x magnification described as squares in Figure A. Scale bars show 50 μm in each photo. C, Quantitative analysis of neointimal area in injured femoral artery. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 6 for Cuff (-), n = 8 for other groups). *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. Cuff (+) Control, †p<0.05 vs. administration of juice of different citrus fruit at same %.