Figure 6.
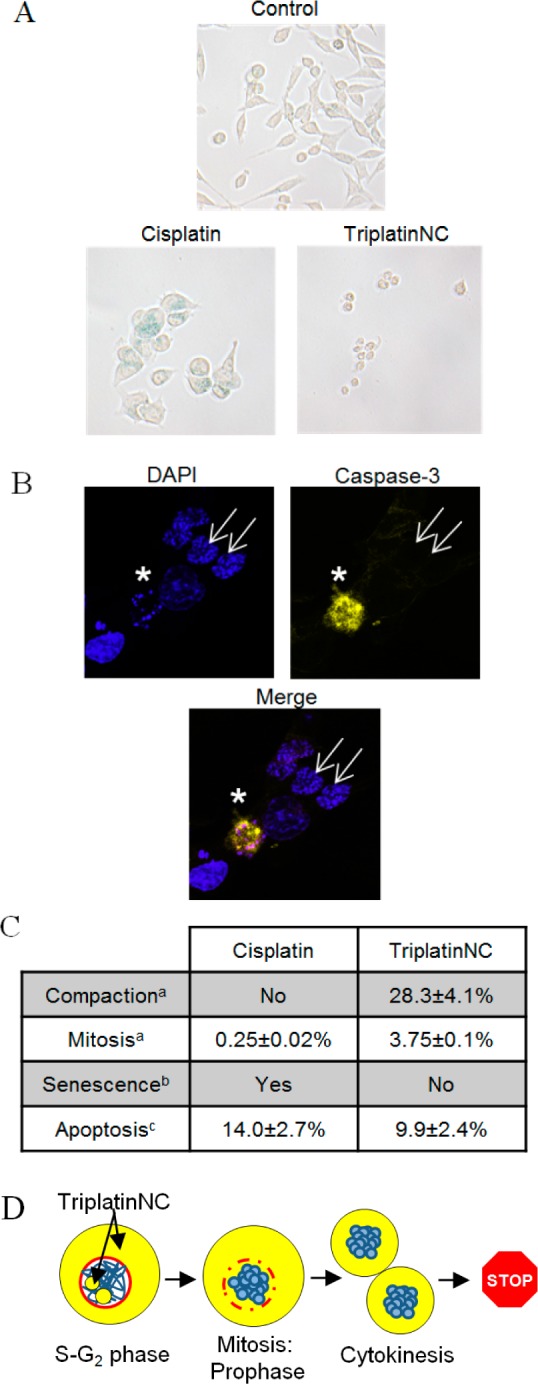
(A) β-Galactosidase activity assay; HCT116 cells were assayed for β-galactosidase activity after treatment with 20 μM cisplatin or TriplatinNC for 96 h. Shown is a representative of two independent experiments. (B) Confocal microscopy; HCT116 cells were treated with 20 μM TriplatinNC for 24 h. Left, top panel; DAPI stained DNA (blue). Right, top panel; cleaved caspase-3 (yellow). Bottom panel; merged DAPI and cleaved caspase-3. Apoptotic cell (white star) containing condensed/fragmented DNA and active caspase-3. Cells with compacted DNA (white arrows) do not contain active caspase-3. (C) Summary; percentage of HCT116 cells undergoing the indicated cellular process after treatment with 20 μM cisplatin or TriplatinNC for 24 h. (D) Schematic; TriplatinNC localizes to the cytoplasm and nucleolus of interphase cells. Cells treated while in S-G2 proceed through mitosis. During prophase, the DNA (blue) condenses and the nuclear membrane (red) disintegrates allowing cytoplasmic pools of TriplatinNC to interact with condensed DNA. Cells undergo cytokinesis; however, the DNA does not decondense or progress through G1. (a) Determined by immunofluorescence: β-tubulin, nucleophosmin/B23, and DAPI DNA staining (Figure 5A,B). (b) Determined by β-galactosidase staining and light microscopy at 200× magnification (panel A). (c) Determined by immunofluorescence; cleaved caspase-3; and DAPI DNA staining. The percentage of cells undergoing apoptosis was determined as the number of cells positive for cleaved caspase-3 divided by the total number of cells. n > 500 cells each for two repeat experiments (Figure 5B).
