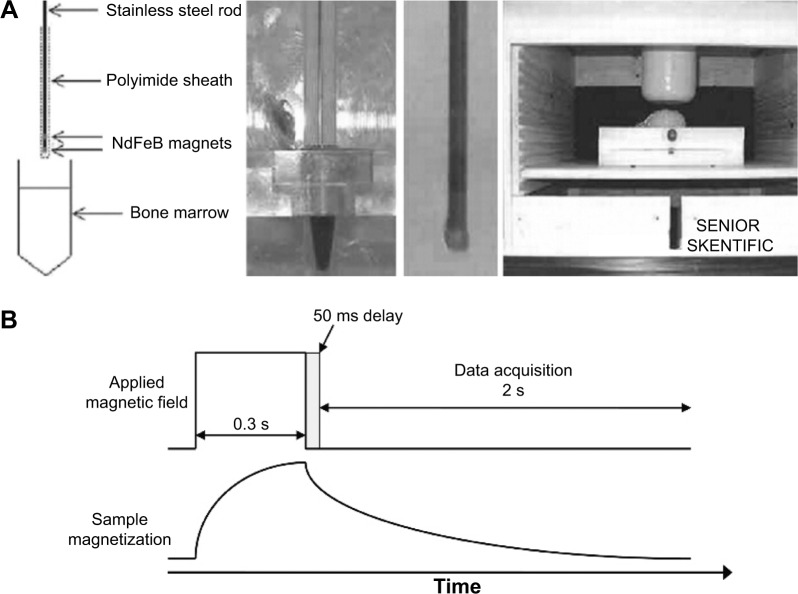
Figure 3.
Illustration of SQUID-relaxometry device to detect SPIONs attached to leukemia cells.
Notes: (A) Description of the magnetic needle used to acquire samples in leukemia patients, (B) Representation of the sample magnetization and data acquisition by SQUID-relaxometry. Reprinted from Elsevier and Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 321(10), Adolphi NL, Huber DL, Bryant HC, et al, Characterization of magnetite nanoparticles for SQUID-relaxometry, 1459–1464, Copyright 2009, with permission from Elsevier.39
Abbreviations: SPIONs, superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles; SQUID, superconductive quantum interference device.