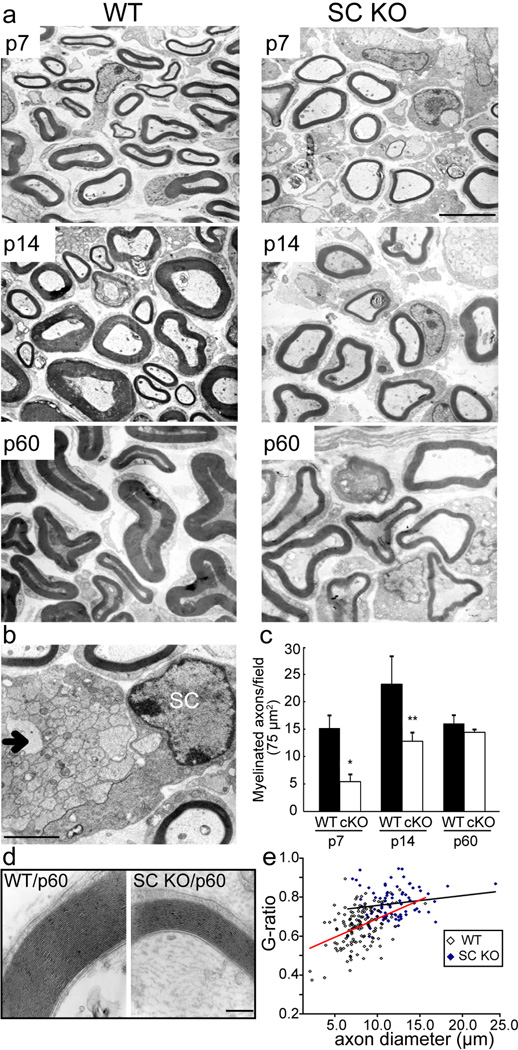
Figure 4. Knockout of LKB1 delays the initiation and alters myelin extent.
(a) The sciatic nerves from SC-specific LKB1 KO and WT littermate mice at postnatal days 7, 14 and 60 days were isolated and processed for electron microscopy. Scale bar = 2.5 µm. (b) Electron micrograph of a sciatic nerve from SC-specific LKB1 KO mouse at 14 days postnatal illustrating a SC nucleus and unmyelinated axons (arrow). Scale bar = 2.5 µm. (c) Quantification of the number of myelinated axons/75 µm2 in the WT littermate (black bars) and the SC-specific LKB1 KO (white bars) at 7, 14, 60 days postnatal. Error bars represent SD. Asterisk represents significance based on Student t-test as compared to the WT control (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). (d) High resolution electron micrographs of myelin from WT littermate and the SC-specific LKB1 KO mice at 60 days postnatal. Scale bar = 200 nm. (e) Determination of myelin sheath thickness by G-ratio quantification from sciatic nerves isolated from three WT and three SC-specific LKB1 KO mice.