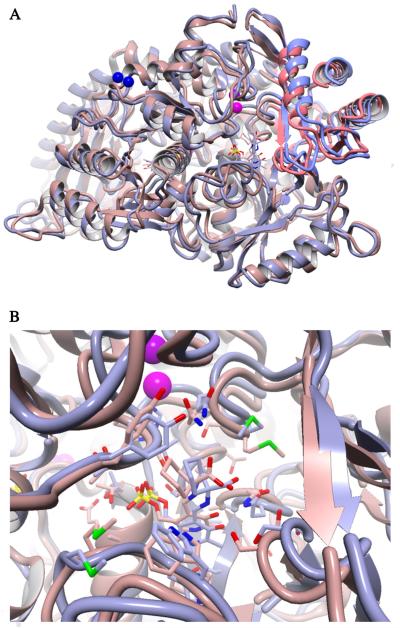
Fig. 5.
Overlay of the structures of WT and the RIVc15 mutant resulting from simulated annealing MD. Both structures contained the external aldimine intermediate of AIB in one active site and that for AC6C in the other. (A) Cartoon view of the structures highlighting the difference in the degree of small domain closure, which is observed in both subunits. The WT structure is shown in mauve with the small domain highlighted in red. The RIVc15 mutant is shown in gray with the small domain highlighted in blue. (B) Active site view of the AC6C external aldimine. The external aldimine positioning in the RIVc15 active site is similar to that of AIB in the WT active site.