Figure 3.
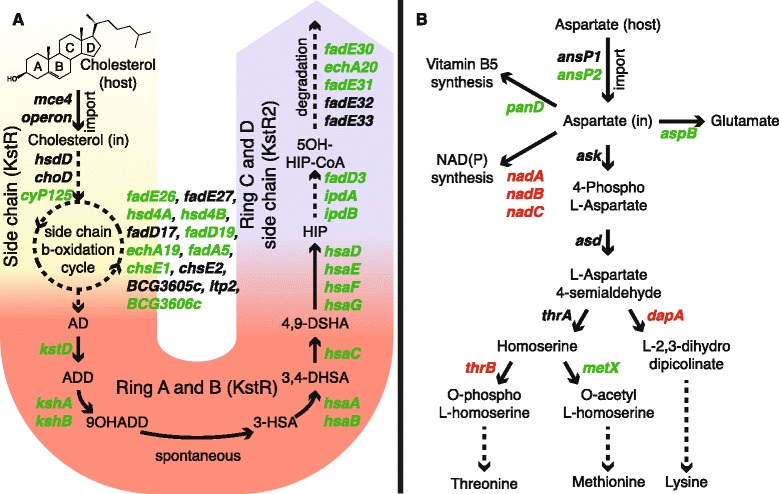
Metabolic processes during infection. Genes in green are induced upon infection (FDR < 0.05), genes in red are repressed (FDR < 0.05) and genes in black show no differential expression. (A) Cholesterol degradation is divided in three parts: The degradation of the side chain (yellow part), degradation of rings A and B (red part) and the degradation of the side chain of rings C and D (blue part). Dashed arrows represent multiple reactions. The degradation of the rings C and D side chain is based on homologous genes from Rhodococcus equi. AD: 4-androstenedione, ADD: 1,4-androstenedione, 9OHADD: 9-hydroxy-1,4, androstene-3-17-dione, 3-HSA: 3-hydroxy-9,10-seconandrost-1,3,5(10)-triene-9,17-dione 3,4-DHSA: 3,4-dihydroxy-9,10-seconandrost-1,3,5(10)-triene-9,17-dione 4,9 DSHA: 4,5-9,10-diseco-3-hydroxy-5,9,17-trioxoandrosta-1(10),2-diene-4-oic acid, HIP: 9,17-dioxo-1,2,3,4,10,19-hexanorandrostan-5-oic acid, 5OH-HIP: 5-hydroxy-methylhexahydro-1-indanone propionate. (B) Aspartate could be imported via AnsP2 and used for the synthesis of vitamin B5, glutamate and methionine. thrB, dapA and nadABC are downregulated, indicating that aspartate is to a lesser extent used to synthesize threonine, lysine and NAD(P).
