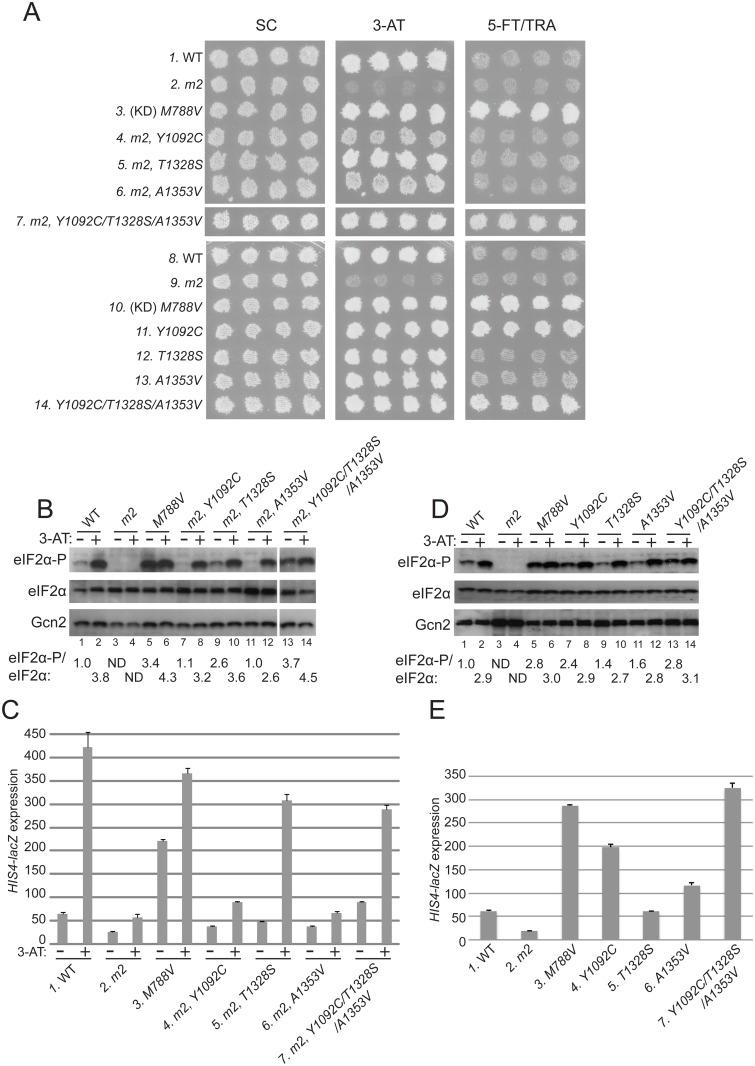
Fig 2. Substitutions in the HisRS domain suppress the m2 mutation and constitutively activate Gcn2 in vivo.
(A) Transformants of gcn2Δ strain H1149 containing derivatives of low-copy plasmid p722 with wild-type GCN2, gcn2-m2, GCN2 c-M788V, or the indicated mutations affecting residues in the HisRS domain either in combination with m2 (rows 4–7) or separated from m2 (rows 11–14) were replica-plated to synthetic complete medium lacking uracil (SC-Ura), SC-Ura plus 30 mM 3-AT, or minimal synthetic medium (SD) supplemented with 0.5 mM 5-FT and 0.125 mM TRA (5FT/TRA) and incubated for 3 d at 30°C. For rows 3 & 10, (KD) signifies a kinase domain substitution by M788V. Images were cropped from results obtained from different plates examined in parallel in the same experiment. (B and D) Cultures of strains from panel A were grown in liquid SC medium lacking uracil and histidine (SC-Ura-His) to saturation, diluted into fresh SC-Ura-His at A600 of ≈0.2, and grown for 6 h at 30°C. 3-AT was added at 10 mM to one culture for 1 h before harvesting (even-numbered lanes). WCEs were resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to Western analysis using the indicated specific antibodies and enhanced chemiluminescence to detect immune complexes. (Note that strains examined in panel B harboring suppressor mutations also contain m2; whereas m2 is absent in the strains analyzed in panel D.) Western signals on the upper panel (eIF2α-P) were quantified by scanning densitometry of exposed films using ImageJ software, normalized for the corresponding signals in the middle panel (total eIF2α), and the mean ratios of the two signals (eIF2α-P/eIF2α) calculated from replicate measurements are indicated below the corresponding lanes. Standard errors are less than 6.5% of the mean values shown. The results in lanes 13–14 were cropped from the same Western blot containing lanes 1–12. (C and E) Strains from (A) were cultured in both nonstarvation and starvation conditions (C), or only in nonstarvation conditions (E), as described in Materials and Methods, and WCEs were prepared and assayed for β-galactosidase activities. Results are the means and S.E.M.s calculated from three transformants, with activity expressed as nanomoles of o-nitrophenyl-β-D-galactopyronoside hydrolyzed per minute per milligram of protein. (Note that strains examined in panel C harboring suppressor mutations also contain m2; whereas m2 is absent in the strains analyzed in panel E.)