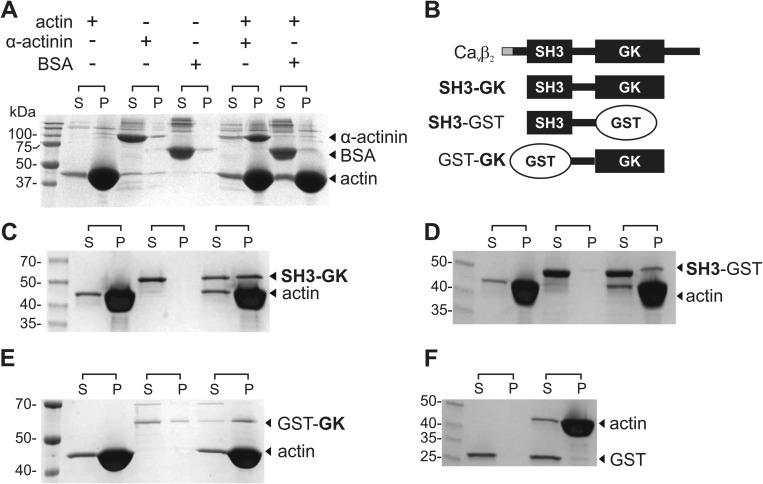
FIGURE 1.
CaVβ associates with actin filaments in vitro. A, F-actin co-sedimentation assay. Actin is dissolved in a polymerization buffer that promotes its filament formation and then is either incubated or not with the test proteins. BSA and α-actinin were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. After centrifugation, the supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions are separated and resolved by SDS-PAGE. Although BSA is always found in the supernatant, the actin-binding protein α-actinin is found in the supernatant in the absence of actin but pelleted after incubation with F-actin. B, schematic of CaVβ2 domain structure and protein constructs used in the co-sedimentation assays. The variable N-terminal segment among the CaVβ2 splice variants is shown in gray. The SH3-GK construct used here is identical for all CaVβ2 variants. C–E, F-actin co-sedimentation assay for the CaVβ2-derived constructs indicated on the right margin. F, GST is not found in the pellet fraction. The numbers denote the molecular mass of standards in kDa. Each assay was repeated three times.