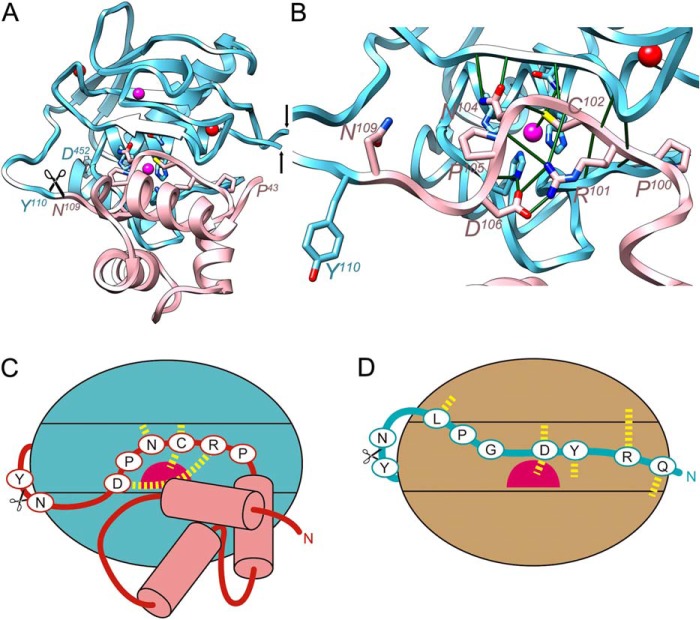
FIGURE 3.
Structural comparison with mammalian pro-MMPs. A, schematic depicting of the structure of pro-MMP-2 (PDB 1EAK (89); MMP-2 residues in italics with superscripted numbering), shown only for its CD (Tyr110-Asp52 in cyan; the fibronectin type-II domains spanning Gln219-Asp92 have been omitted, the black arrows pinpoint the insertion points) and prodomain (Pro43-Asn109 in pink, without the first 11 residues in extended conformation). The orientation displayed corresponds to that of Fig. 2A after applying a horizontal rotation of 15°. Residues of the conserved motif (Pro100-Asp106) key for structural integrity of the inhibitory segment are depicted for their side chains. B, close-up of A after removal of prodomain segment Pro43-Asn66 to provide insight into the interactions of the conserved motif. Key electrostatic interactions are shown as green lines. The catalytic glutamate, Glu404, is replaced by a glutamine, the histidines from the CSBZ are His403, His407, and His413. C and D, scheme depicting the interaction modi of the propeptides of pro-MMP-2 through a cysteine-switch mechanism (C) and pKly18 through an aspartate-switch mechanism (D). The catalytic zinc ions are shown as magenta spheres and relevant interactions are shown as yellow dashed lines.