FIGURE 4.
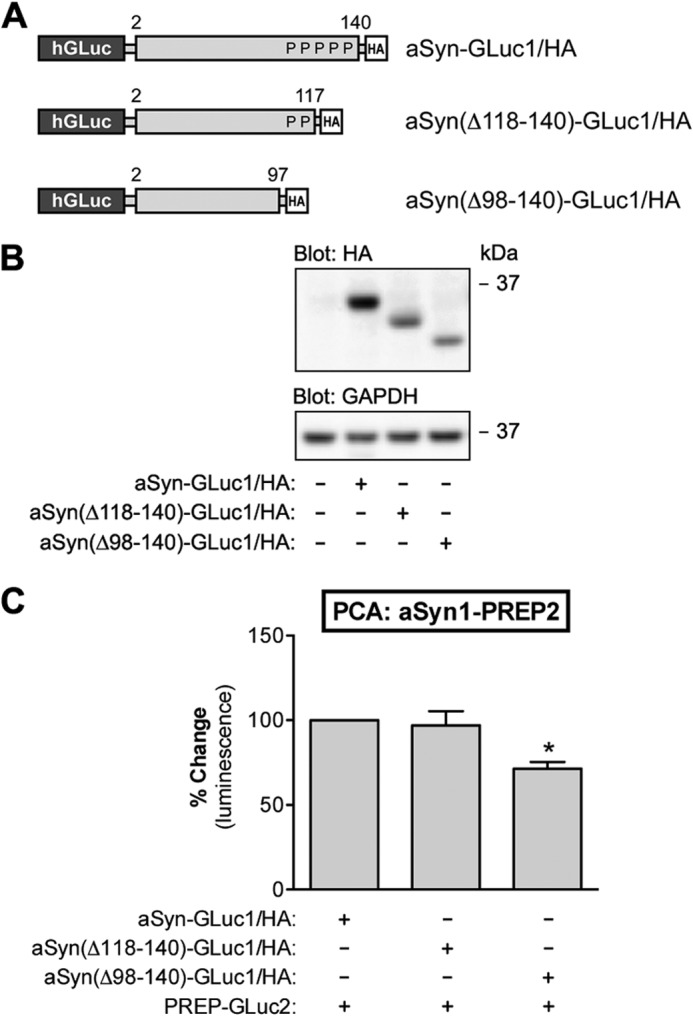
aSyn-PREP interaction does not require the proline-rich C-terminal domain of aSyn. A, schematic presentation of GLuc fragment-tagged aSyn constructs with different C-terminal truncations used in this study. P indicates a proline residue in the C-terminal tail of aSyn. B, the expression aSyn-GLuc1, aSyn(Δ118–140)-GLuc1, and aSyn(ΔC98–140)-GLuc1 was analyzed by Western blot. Each plasmid was transfected at 1.5 μg per well. All the constructs were appropriately expressed in N2A cells as determined by the anti-HA staining of the Western blot. GAPDH served as a loading control. C, the effect of C-terminal truncation of aSyn on aSyn-PREP interaction was studied by PCA. Co-expression of PREP-GLuc2 with aSyn(ΔC118–140)-GLuc1 showed similar PCA signal as the full-length aSyn-GLuc1, but co-expression of PREP-GLuc2 with aSyn(ΔC98–140)-GLuc1 showed a decrease in PCA signal. However, this may be due to the lower expression level of aSyn(Δ98–140) as compared with the full-length aSyn-GLuc1 reporter (B). The average values are displayed as percent change as compared with the control (mean ± S.E.; n = 3 independent experiments). * indicates significant difference with p < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA).
