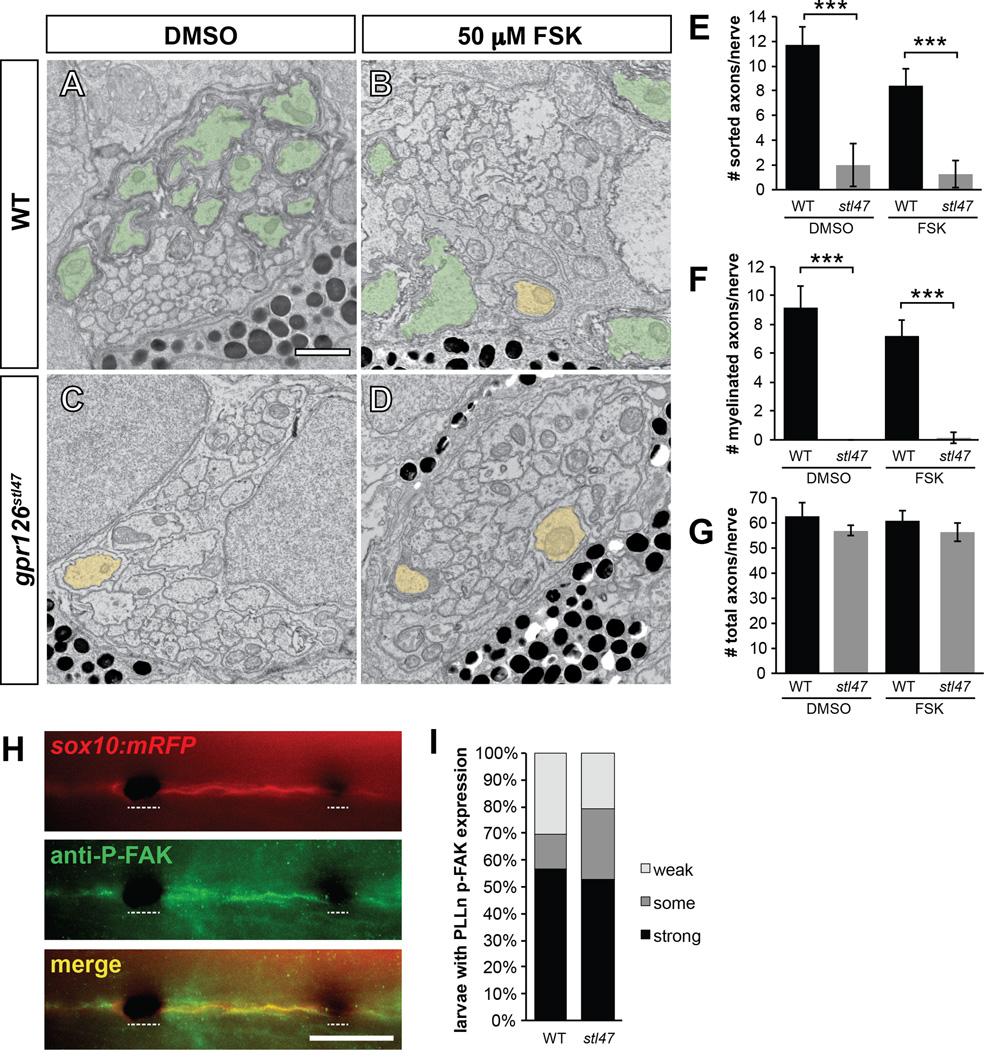
Figure 2. Gpr126-NTF radial sorting occurs independently of Gpr126-CTF and p-FAK signalling.
(A–D) TEM of 5 dpf zebrafish showing cross-sections through PLLn. Sorted and myelinated axons are defined and pseudocolored as in Figure 1. Scale bar = 1 µm. (A) Radial sorting and myelination are observed in WT siblings treated with DMSO and (B) 50 µM forskolin (FSK). (C) Radial sorting and myelination are impaired in gpr126stl47 zygotic mutant siblings treated with DMSO and (D) FSK. (E–G) Quantification of TEM images. Bars represent means ± SD. *** p<0.001, 1-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. (E) Number of sorted axons per PLLn. (F) Number of myelinated axons per PLLn. (G) Number of total axons per PLLn. (H) Phosphorylated FAK (P-FAK) immunostaining (green) labels PLLn SCs of a 4 dpf WT Tg(sox10:mRFP) larva (red). Dotted lines indicate regions where pigment cells obscure fluorescence. Scale bar = 100 µm. (I) Quantification of p-FAK levels expressed as a percentage of larvae with SC-specific p-FAK immunostaining along the PLLn in WT and gpr126stl47 mutants. No significant difference was observed in either genotype.