Figure 1.
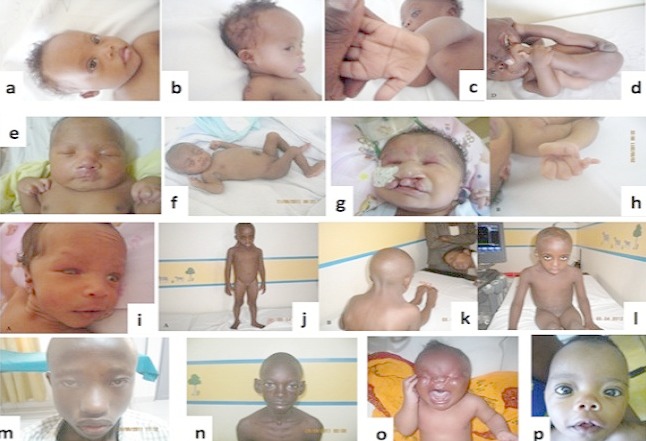
Patient photos with characterized different syndromes. Patients affected by Down syndrome. (a) hypertelorism, flat nasal bridge, short neck, mongoloid slant; (b) low set ears and protruding tongue; (c) single palmar crease and (d) hyperflexibility; (e) Patient affected by Edwards syndrome, note the presence of hypertelorism, flat nasal bridge, short neck, clenched hands with overlapping fingers; (f) umbilical hernia and club feet; (g) Patient affected by Patau syndrome with typical facial dysmorphism characterized by hypertelorism, cleft lip and palate; (h) and polydactyly; (i) Patient with Cat eye syndrome showing right preauricular tag, right microphthalmia and coloboma; (j) Patient affected by Turner syndrome presenting with short stature; (k) webbed neck and (l) wide spaced nipples; (m) Patient affected by DiGeorge syndrome. Note the presence of long face, hypertelorism, proeminent nose with squared nasal root; (n) Patient affected by Williams-Beuren syndrome presenting periorbital fullness (puffiness around the eyes), long philtrum, wide mouth, large and protruding ears; (o) Patient with Fraser syndrome showing cryptophthalmos, ears abnormalities and syndactyly; (p) Patient affected by Noonan syndrome with physical facial signs showing hypertelorism, long philtrum and proeminent upper lip
