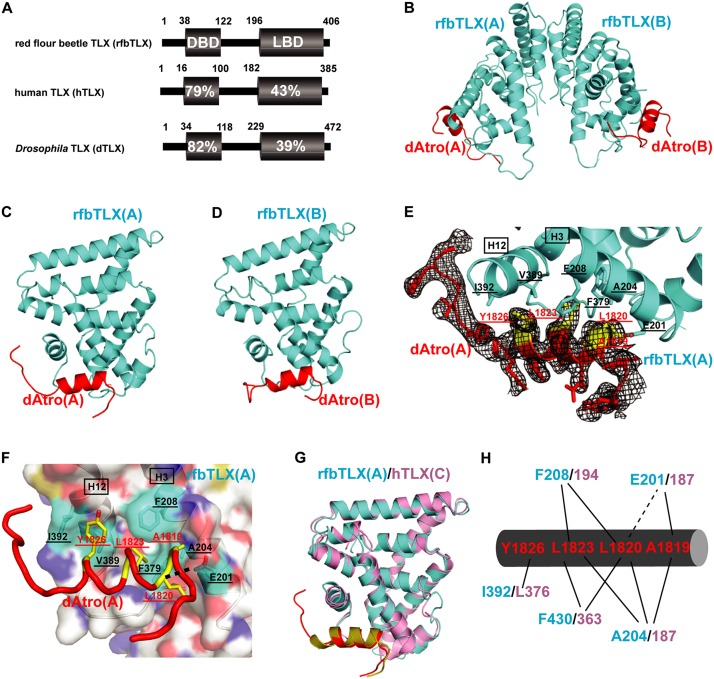
Figure 2.
Structural analysis of the rfbTLX–Atro box complex. (A) Sequence identities of rfbTLX (NP_001034502), dTLX (NP_524596), and hTLX (NP_003260). Numbers refer to the amino acid position in the DBD or LBD of each TLX protein. (B) A ribbon model of rfbTLX (cyan) in complex with peptide dAtro (red). rfbTLX forms a dimer via the helix H10–H10 interaction. MBP has been omitted from the structure. (C) A ribbon model of rfbTLX(A) in complex with peptide dAtro. (D) A ribbon model of rfbTLX(B) in complex with peptide dAtro. (E) Representative Fo − Fc electron density omit map contoured at 1.0 σ for peptide dAtro(A) (red). The dAtrophin amino acids involved in hTLX binding are highlighted in yellow, labeled in red, and underlined. dAtrophin-binding amino acids in hTLX are labeled in black and underlined. They are contributed to by helices H3 and H12, which are labeled in black and boxed, and also by the loop between H11 and H12. (F) Close-up presentation of the rfbTLX/Atrophin interface. rfbTLX amino acids involved in the interaction are marked by a cyan transparent surface, labeled in black, and underlined. dAtrophin amino acids involved in the interaction are marked in yellow, labeled in red, and underlined. The black dashed line represents the H bond interaction between rfbTLX and Atrophin. (G) A ribbon model of rfbTLX (complex A; cyan) superposed to hTLX (complex C; pink). Peptide dAtro (complex A) bound to rfbTLX (complex A) is shown in red, and peptide dAtro (complex C) bound to hTLX (complex C) is shown in yellow. (H) Schematic presentation of the interactions between rfbTLX/hTLX and peptide dAtro. dAtro residues are labeled in red, rfbTLX residues are shown in cyan, and human residues are labeled in pink. Hydrophobic interactions are illustrated by solid lines, and H bonds are indicated by dashed lines.