Figure 5. Deletion of exon 45–55 region in human DMD myoblasts by multiplex CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing.
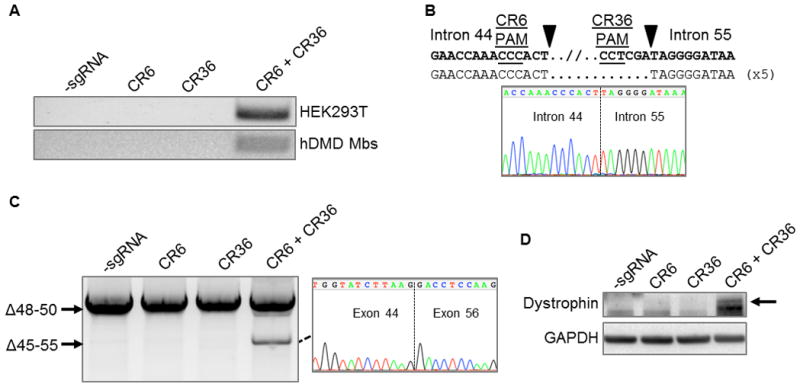
(A) End-point genomic PCR of genomic DNA to detect deletion of the region between intron 44 and intron 55 after treating HEK293Ts or DMD myoblasts with the indicated sgRNAs. (B) Individual clones of PCR products of the expected size for the deletions from DMD myoblasts in (A) were analyzed by Sanger sequencing to determine the sequences of genomic deletions present at the targeted locus. Below is a representative chromatograms showing the sequence of the expected deletion junctions. (C) End-point RT-PCR analysis of dystrophin mRNA transcripts in CRISPR/Cas9-modified human Δ48–50 DMD myoblasts treated with the indicated sgRNAs. A representative chromatogram of the expected deletion PCR product is shown at the right. (D) Analysis of restored dystrophin protein expression by western blot following electroporation of DMD myoblasts with sgRNAs targeted to intron 44 and/or intron 55.
