Figure 1.
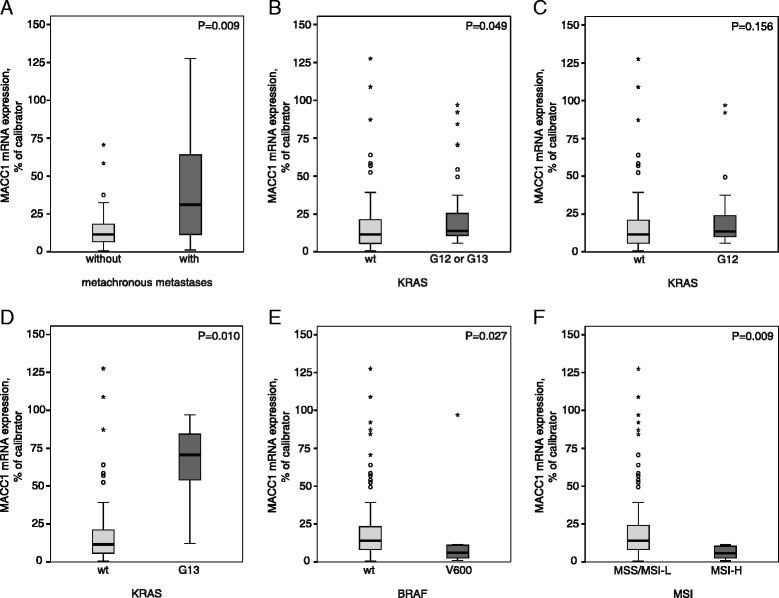
Associations of MACC1 expression with KRAS mutation, BRAF mutation or MSI status. MACC1 mRNA expression levels of the tumors were quantified using quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR [9]. Tumor DNA was extracted and subjected to PCR for amplification of KRAS and BRAF sequences and analyzed by sequencing [15]. MSI Analysis System was used for MSI status determination as described previously [16]. Tumors were discriminated in Microsatellite stable (MSS)/MSI-low (MSI-L; 0 or 1 markers demonstrating instability) or MSI-High (MSI-H; two or more markers instable). A Significantly increased MACC1 mRNA expression levels were detected in primary tumors of patients with metachronous metastases (P = 0.009). B MACC1 expression level was significantly increased in KRAS mutated (G12 or G13) tumors compared to tumors with KRAS wild type (KRAS wt) (P = 0.049). C There were no significant differences of MACC1 expression in KRAS G12 mutated compared to KRAS wt tumors (P = 0.156). D Primary tumors harboring G13 mutated KRAS showed a significantly increased MACC1 expression level (P = 0.010). E In BRAF wt tumors MACC1 expression was significantly increased compared to BRAF V600 mutated tumors (P = 0.027). F MACC1 expression of MSS/MSI-L tumors was significantly increased compared to MSI-H tumors (P = 0.009). Significance in differential mRNA expression was determined by Mann–Whitney U-test. Calculation of q-values from the corresponding P-values was performed to control for the false discovery rate (FDR) [17]. FDR-adjusted P-values less than 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant.
