Figure 9.
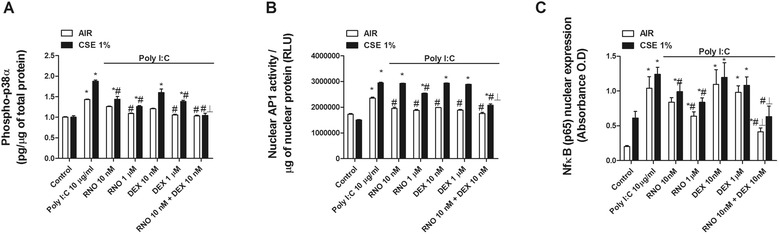
Roflumilast N-oxide shows additive or synergistic effects with dexamethasone in inhibiting p38, AP1 and NF-κB induced by TLR3 stimulation. BEAS2B cells were pretreated with or without cigarette smoke extract (CSE) 1% for 1 hour followed by the incubation in the presence or absence of different concentrations of roflumilast N-oxide (RNO) or dexamethasone (DEX) for 1 hour. After drug incubation cells were stimulated with the TLR3 agonist poly I:C for 30 minutes (A), 45 minutes (B), or 1 hour (C), and total protein (A) or nuclear protein (B, C) was extracted to measure p38 phosphorylation, AP1 nuclear activation, or NF-κB (p65) nuclear expression. Each graph represents the mean ± SEM of 3–4 independent experiments. One-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) were performed. Post hoc Bonferroni test: *P < 0.05 compared with control; #P < 0.05 compared with stimulus; ┸P < 0.05 compared with monotherapy.
