Figure 4. Antioxidant genes become upregulated in adult clk-1 worms.
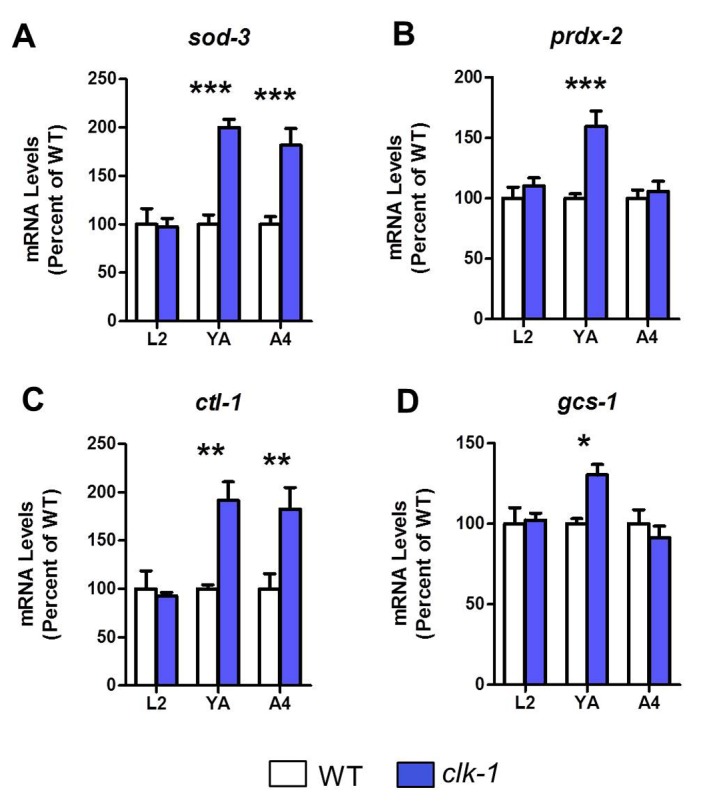
To determine whether the upregulation of antioxidant genes could explain the resistance of clk-1 worms to chronic oxidative stress during adulthood, we examined the time course of gene expression changes in clk-1 worms. We examined worms at three time point: L2 worms (L2), day 1 adult worms (YA) and day 4 adult worms (A4) by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. The antioxidant genes sod-3 (A), prdx-2 (B), ctl-1 (C) and gcs-1 (D) were not upregulated at the L2 phase, but were increased in young adult worms. Thus, there is an increase in antioxidant gene expression at the start of adulthood that corresponds to the increased resistance to chronic oxidative stress in clk-1 worms. Error bars indicate SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001.
