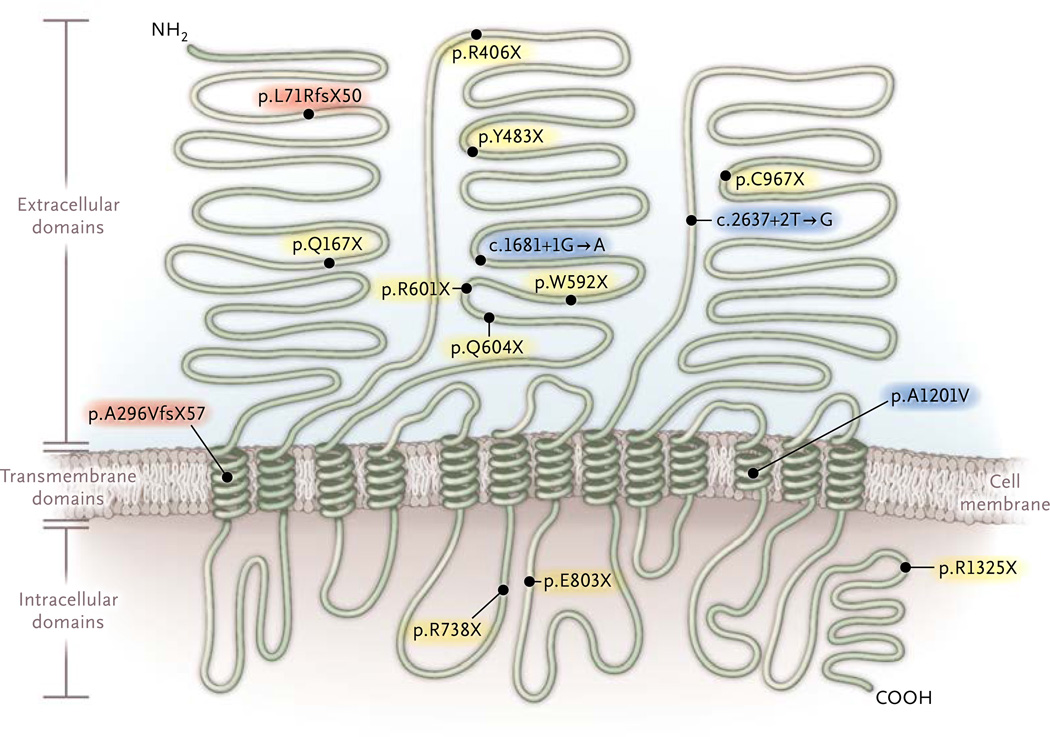
Figure 1. Inactivating Mutations in NPC1L1 Identified in the Study.
Black circles indicate individual mutations along with the effect expected to lead to NPC1L1 inactivation. Mutations p.L71RfsX50 and p.A296VfsX57 (red shading) are indels that shift the open reading frame and induce a premature termination codon after an additional 50 and 57 amino acids, respectively. Mutations c.1681+1G→A, c.2637+2T→G, and p.A1201V (c.3602C→T) (blue shading) alter the splicing process at sites of modification of the nascent pre-messenger RNA transcript (splice-site mutations). All other mutations (yellow shading) are single-nucleotide variants that introduce a termination codon. The locations of the three main extracellular domains, 13 transmembrane domains, and intracellular domains are based on data from Betters and Yu.27 NH2 denotes the N-terminal at which protein translation is initiated, and COOH the C-terminal at which translation terminates.