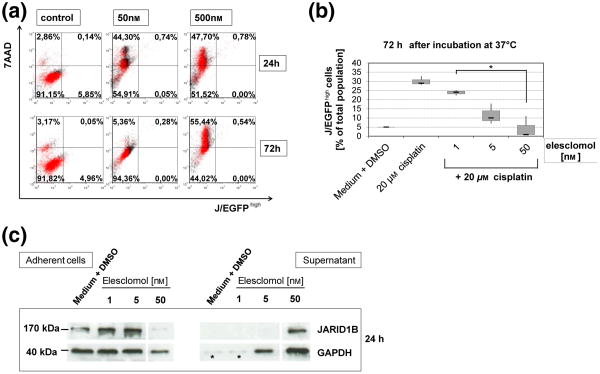
Figure 1.
Elesclomol prevents the survival of intrinsically resistant melanoma cells. (a) Elesclomol treatment eliminates the slow-cycling melanoma cell subpopulation as indicated by the loss of J/EGFPhigh WM3734 cells in flow cytometry (lower right quadrant). 7AAD was used as marker for cell death. (b) The relative percentage of therapy resistant J/EGFPhigh cells among the viable cell fraction increases under treatment with cytotoxic drugs like cisplatin, but decreases again under co-treatment together with elesclomol (P < 0.05). Box plots were calculated from three independently performed flow cytometric experiments. (c) Immunoblots confirm that JARID1B-expressing cells are effectively killed by elesclomol leading to their cell detachment into the culture supernatant. As indicated by the loading controls (see asterisks), there was not enough overall cell killing below 5 nM of elesclomol to load equal protein amounts.