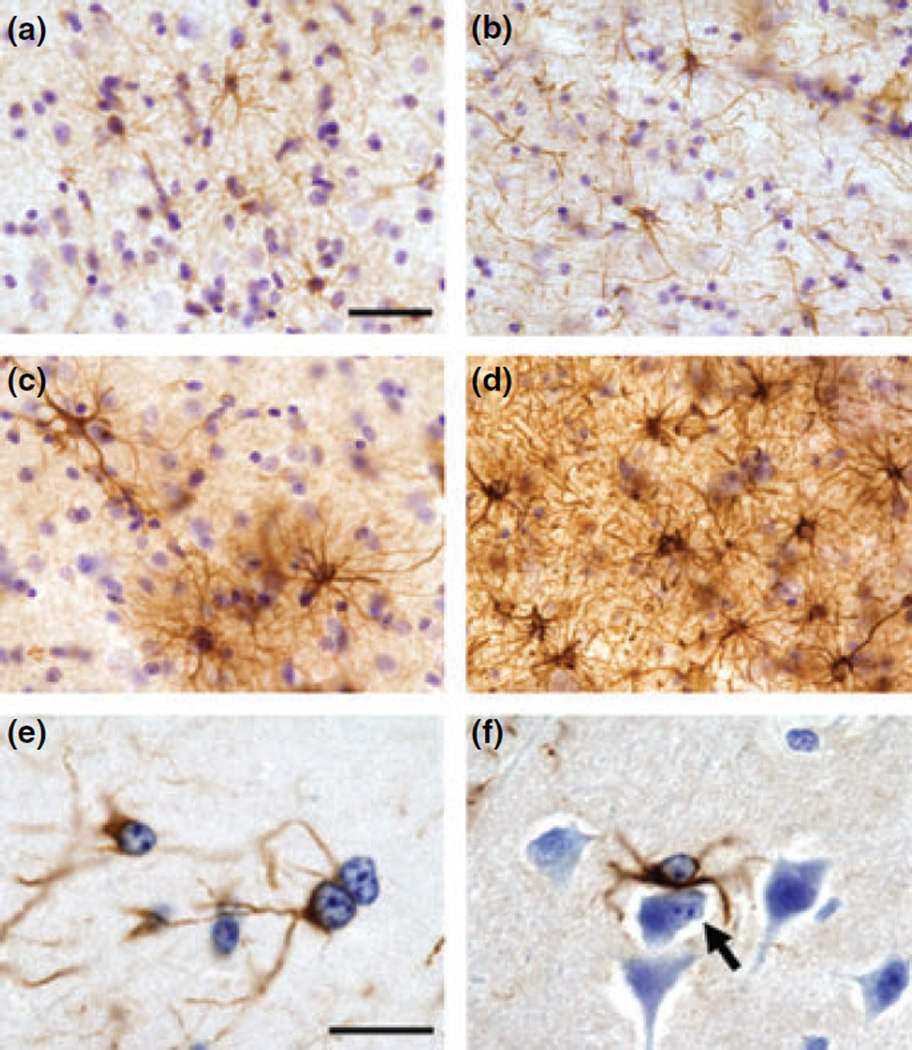
Fig. 5.
Representative images of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunohistochemistry in control (a and b) and Mn-exposed (c–f) frontal cortex. In control animals, astrocytes expressed a normal ramified morphology in the gray (a) and white matter (b). In Mn-exposed frontal cortex, there were areas in which GFAP-labeled astrocytes were increased in number and expressed hypertrophic processes in both the gray (c) and white matter (d). Alzheimer’s type II astrocytes were frequently observed in Mn-exposed animals (e and f). Alzheimer’s type II astrocytes are often paired (see adjacent cells in e) and express enlarged nuclei with prominent nucleoli. In panel (f), there is an Alzheimer’s type II astrocyte adjacent to a cell undergoing apoptosis (arrow in f). Scale bar: (a–d) 40 and (e and f) 20 µm.