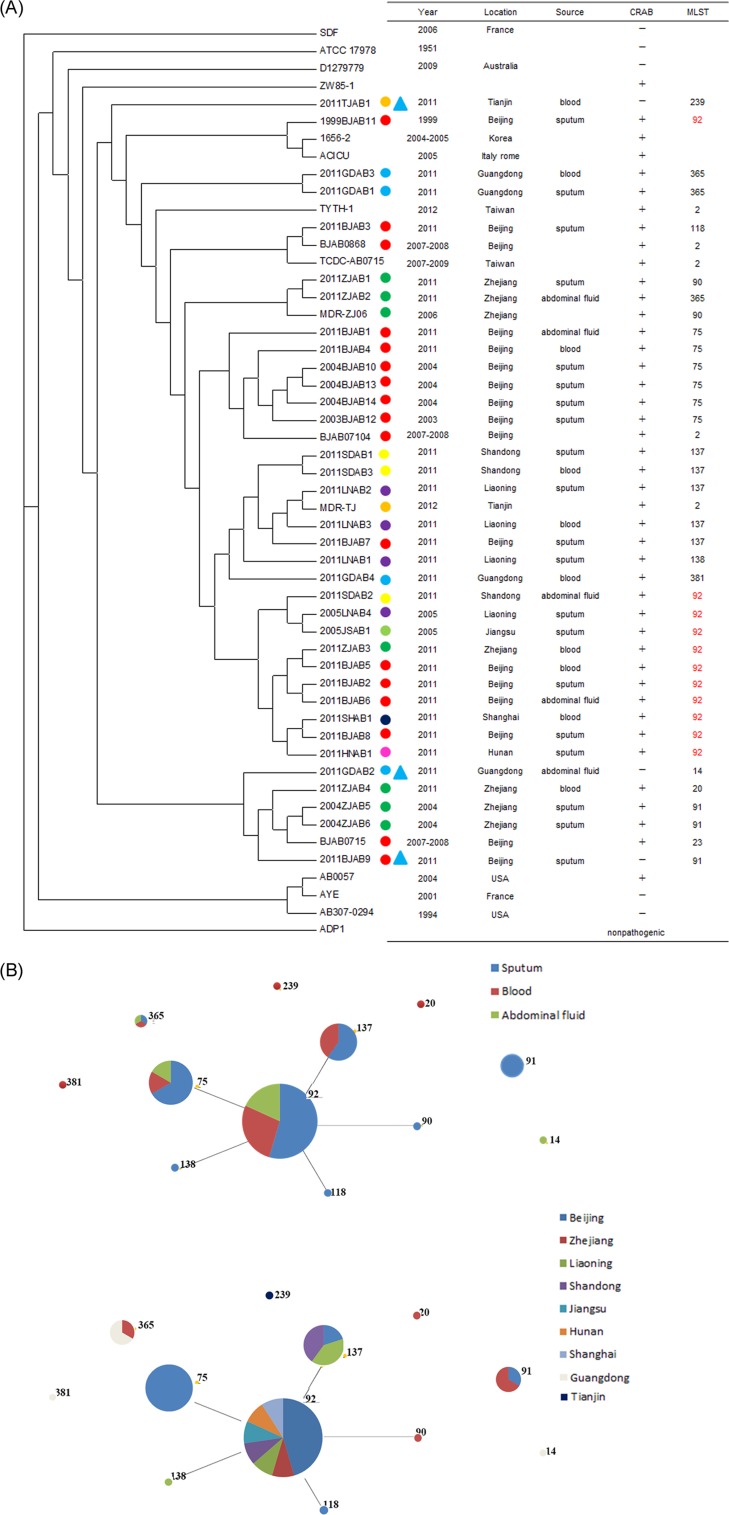
FIG 1.
(A) Whole-genome phylogeny of the genomes of the 35 A. baumannii strains evaluated in this study and 17 sequenced A. baumannii genomes. The phylogeny tree was constructed on the basis of SNPs and was rooted with A. baylyi ADP1. Colored circles, the different locations of the strains isolated; blue triangles, the strains were susceptible to carbapenems. The predominant MLST, ST92, is highlighted in red. (B) Results of eBURST analysis conducted to assign CCs to the 35 A. baumannii strains utilizing seven loci. The CCs are indicated by circles, and the predicted clonal ancestors are shown by the central circles. Numbers indicate the MLST type. The sizes of the points are proportional to the number of isolates assigned to each MLST type.