FIG 7.
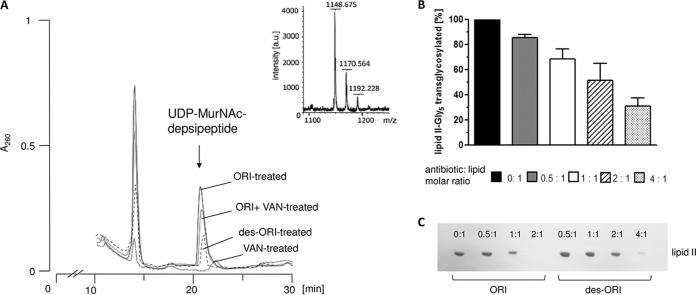
Intracellular accumulation of the soluble cell wall precursor UDP-MurNAc-depsipeptide in VanA-type E. faecium. (A) E. faecium BM4147 was grown in HHD broth (0.002% Tween 80) to an OD600 of 0.5 and supplemented with 80 mg/liter vancomycin (VAN) to induce vanA expression. After 10 min, oritavancin (ORI) or des-N-methylleucyl-oritavancin (des-ORI) was added at 10× MIC and incubated for 60 min. Cells were harvested and extracted with boiling water, and the intracellular nucleotide pool was analyzed by reversed-phase HPLC. UDP-MurNAc-depsipeptide (UDP-MurNAc-l-Ala-d-Gln-l-Lys-d-Ala-d-Lac) was identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. (B) Inhibition of the PBP2-catalyzed reaction by des-ORI in vitro. The conversion of [14C]lipid II-Gly5 into polymeric peptidoglycan in the presence of increasing concentrations of des-ORI was quantitatively analyzed by applying the reaction mixtures directly onto TLC plates and subsequent separation in solvent B (butanol-acetic acid-water-pyridine [15:3:12:10, vol/vol/vol/vol]) followed by the detection and quantification of residual [14C]lipid II-Gly5 using phosphorimaging. (C) Purified lipid II was incubated with increasing concentrations of ORI or des-ORI at molar ratios of 0.5 to 4:1 with respect to the substrate lipid II. The reaction mixtures were extracted, and unbound lipid was analyzed by TLC and visualized by PMA staining.