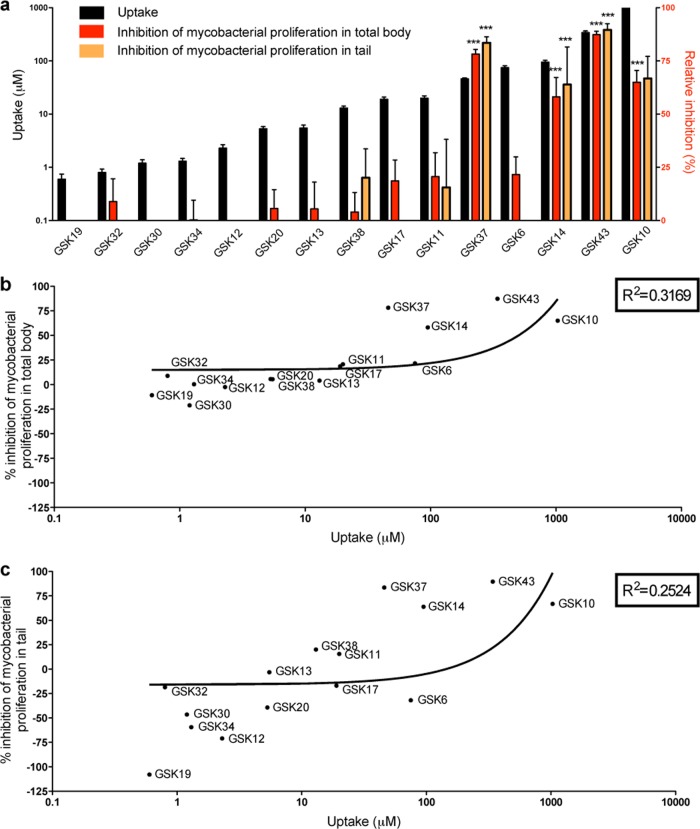
FIG 3.
Correlation between the uptake level of preclinical antitubercular compounds and their efficacy in M. marinum zebrafish infection model. (a) Uptake levels of 15 preclinical antitubercular GSK compounds were measured from samples taken from the yolk of 5-day-old zebrafish larvae after 40 h of exposure at 10 μM concentration (black bars) (n = 10). The efficacy of the compounds was assessed by monitoring fluorescent bacterial burden in the total body (red bars) or tail region (orange bars) of larvae at 5 days p.i. using the COPAS system after 40 h of treatment (n = 200). Efficacy is expressed as a percentage of inhibition of mycobacterial proliferation relative to the level for DMSO-treated control groups. The bar graphs depict the correlation between the uptake and the relative inhibition, both in the total body and the tail region. Significance in inhibition is indicated with asterisks (***, P < 0.001). (b and c) Correlation between the efficacy in the total body (b) or in the tail (c) and the uptake of the GSK compounds. The efficacy of several compounds shown in panels b and c is below detection limits, as shown in panel a.