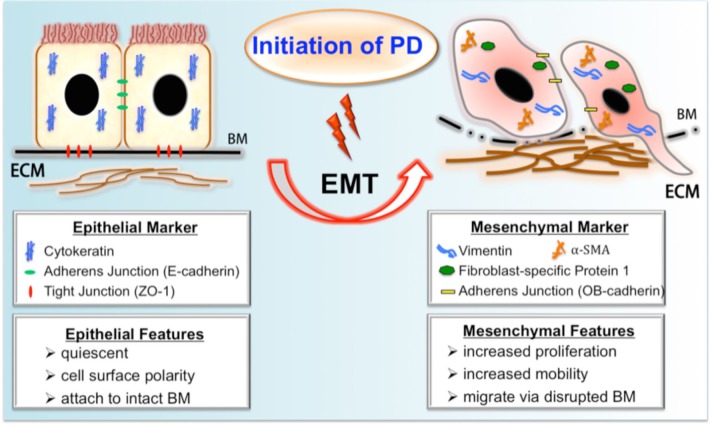
FIGURE 1 —
A schematic summary of fibrogenic EMT during PD. Upon exposure to PD, the peritoneal mesothelial cell undergoes profound phenotypic changes of EMT, resulting in the loss of epithelial features and the gain of mesenchymal characteristics. The process of EMT includes downregulation of epithelial adherens junction (like E-cadherin) and tight junction components (like ZO-1) and upregulation of mesenchymal junctional proteins (like OB-cadherin). Thereafter, the main cytoskeletal protein pattern of epithelium is switched from cytokeratin to vimentin with de novo synthesis of FSP-1 and α-SMA. A subset of transitioning cells with increased mobility might migrate into the submesothelial zone through disrupted BM and contribute to the increased deposition of ECM. PD = peritoneal dialysis; EMT = epithelial-mesenchymal transition; BM = basement membrane; ECM = extracellular matrix; ZO-1 = zonula occludens-1; FSP-1 = fibroblast-specific protein 1; α-SMA = α smooth muscle actin.