Table 3.
Comparisons between the three processes of AOM: S-DAMO, N-DAMO, and M-DAMO
| Features | S-DAMO | N-DAMO | M-DAMO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Habitat | Marine environments and freshwater environments | Freshwater environments | Marine environments |
| Mechanism hypothesis | Reverse methanogenesis, acetogenesis, and methylogenesis | Aerobic methane oxidation and reverse methanogenesis | ND |
| Electron acceptor | 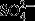 |
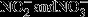 |
Mn4+ and Fe3+ |
| Responsible microbes | ANME | M. oxyfera and M. nitroreducens | MBGD (possible) |
| Reaction (AOM) |
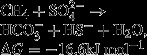 (eq. 3) (eq. 3) |
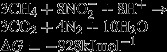 (eq. 12) and (eq. 12) and |
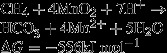 (eq. 14) and (eq. 14) and |
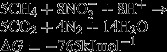 (eq. 13) (eq. 13) |
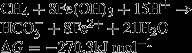 (eq. 15) (eq. 15) |
S-DAMO, sulfate-dependent anaerobic methane oxidation; N-DAMO, nitrate/nitrite-dependent anaerobic methane oxidation; M-DAMO, metal ion (Mn4+ and Fe3+)-dependent anaerobic methane oxidation; ANME, anaerobic methanotrophic archaea; M. oxyfera, Candidatus Methylomirabilis oxyfera; M. nitroreducens, Candidatus Methanoperedens nitroreducens; MBGD, marine benthic group D; ND, not determined; AOM, anaerobic oxidation of methane.
