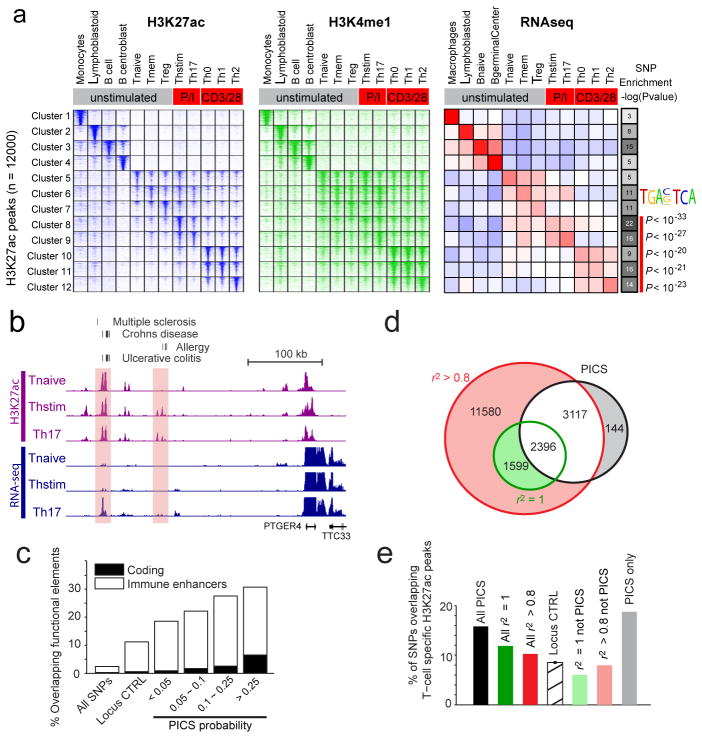
Figure 2. Epigenetic fine-mapping of enhancers.
a, Heatmaps show H3K27ac and H3K4me1 signals for 1000 candidate enhancers (rows) in 12 immune cell types (columns). Enhancers are clustered by the cell type-specificity of their H3K27ac signals. Adjacent heatmap shows average RNA-seq expression for the genes nearest to the enhancers in each cluster. Gray-scale (right) depicts the enrichment of PICS autoimmunity SNPs in each enhancer cluster (hypergeometric p-values calculated based on the number of PICS SNPs overlapping enhancers from each cluster, relative to random SNPs from the same loci). The AP-1 motif is over-represented in enhancers preferentially marked in stimulated T-cells, compared to naïve T-cells. b, Candidate causal SNPs displayed along with H3K27ac and RNA-seq signals at the PTGER4 locus. A subset of enhancers with disease variants (shaded) shows evidence of stimulus-dependent eRNA transcription. c, Stacked bar graph indicates percentage overlap with immune enhancers and coding sequence for PICS SNPs at different probability thresholds, compared to control SNPs drawn from the entire genome (All SNPs) or the same loci (Locus CTRL). d, Venn diagram compares PICS SNPs to GWAS catalog SNPs with indicated r2 thresholds. e, Bar graph indicates percentage overlap with annotated T-cell enhancers for PICS SNPs, GWAS SNPs at indicted thresholds, locus control SNPs, and three subsets of SNPs defined and shaded as in panel d.