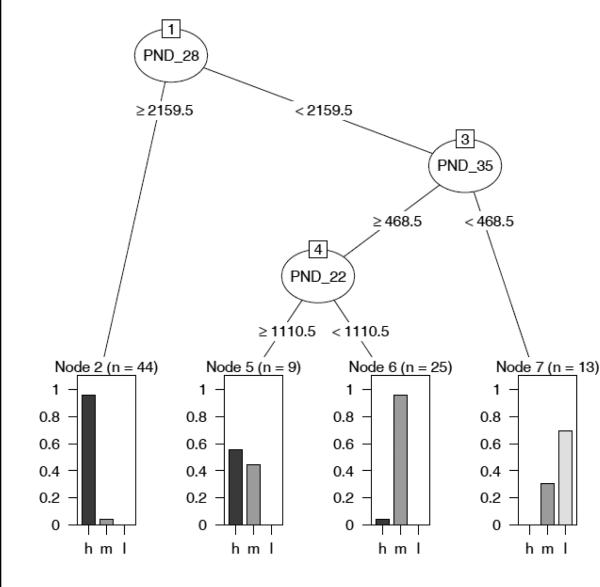
Figure 7.
A classification tree based on stereotypy counts at each of eight developmental time points and predicted trajectory. The tree represents binary splits (nodes) that separate the mice into final groupings (end nodes) which are optimally homogenous in regards to predicted trajectory. Restrictions are put on the splits to prevent overly small end nodes and guard against overfitting. The tree shows that time points PND 28, PND 35, and PND 22 were most informative in determining mouse trajectories (h, m, l or high frequency, mid frequency, low frequency).