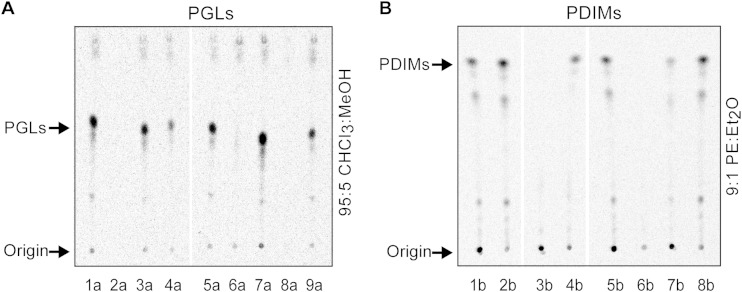
FIG 5.
Mutational analysis points at M. marinum FadD29 as a PHPA-AMP ligase candidate. Radio-TLC analysis of 14C-labeled PGLs (A) and 14C-PDIMs (B) from M. marinum wt + pCP0 (lanes 1a, 5a, 1b, 5b), M. marinum ΔfadD22 + pCP0 (lanes 2a and 2b), M. marinum ΔfadD22 + pCP0-fadD22 (lane 3a), M. marinum ΔfadD26 + pCP0 (lanes 4a and 3b), M. marinum ΔfadD26 + pCP0-fadD26 (lane 4b), M. marinum ΔfadD28 + pCP0 (lanes 6a and 6b), M. marinum ΔfadD28 + pCP0-fadD28 (lanes 7a and 7b), M. marinum ΔfadD29 + pCP0 (lanes 8a and 8b), and M. marinum ΔfadD29 + pCP0-fadD29 (lane 9a). The wild-type (wt) and mutant M. marinum strains carried the vector pCP0 so they could be cultured in the same kanamycin-containing medium used for the complemented strains. The TLC solvent systems used are as described for Fig. 4.