Figure 2. Metrnl is expressed by alternatively activated macrophages (AAM/M2).
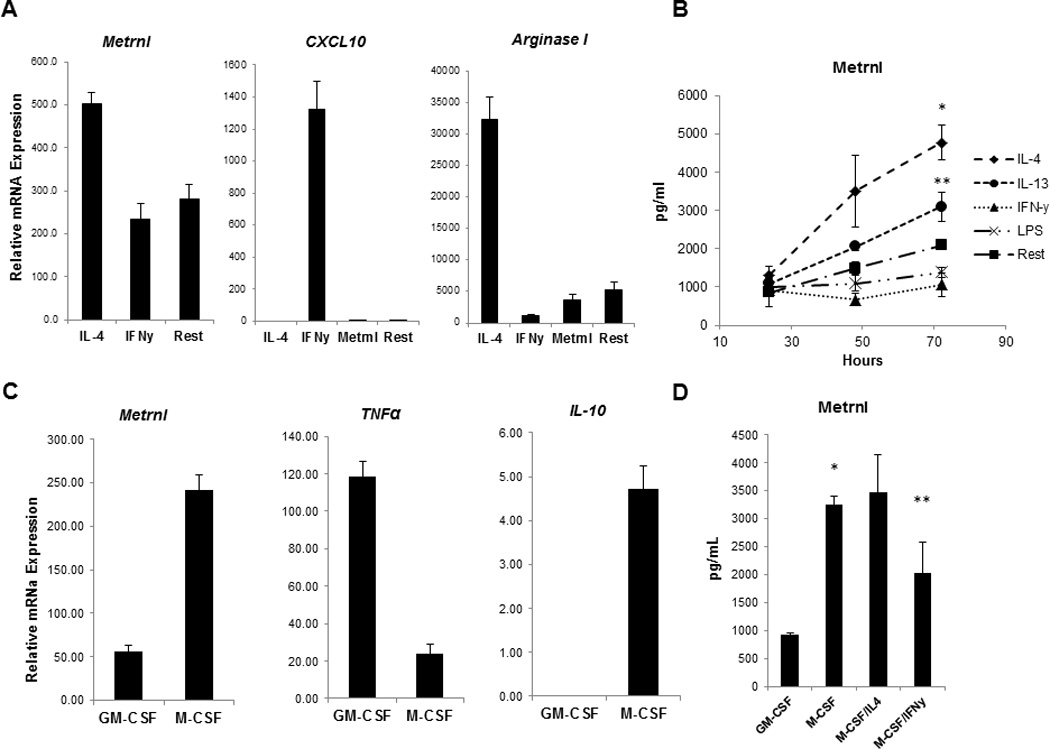
(A) Peritoneal exudate macrophages from C57BL mice were cultured under either M1 (IFNγ) or M2 (IL-4) polarizing conditions. 8 hours post stimulation Metrnl expression was measured by Q-PCR. Metrnl expression was elevated in response to IL-4 and it was suppressed by IFNγ. M1 marker CXCL10 and M2 markers Arginase I were measured in the polarized macrophages to confirm successful polarization.
(B) Metrnl protein levels were measured by ELISA in supernatants from macrophages cultured in the presence of IL-4, IL-13, IFNγ and LPS for 24, 48 and 72hrs. Production of Metrnl was increased in peritoneal cavity macrophages in response to IL-4 (*P < 0.001) and IL-13 (**P < 0.02).
(C) The Metrnl expression levels were measured Q-PCR in GM-CSF -or M-CSF– derived BMM (GM-BMM and BMM, respectively). Metrnl was elevated in BMM and paralleled expression of another BMM cytokine (IL-10).
(D) Metrnl levels were measured by ELISA in GM-BMM and BMM. Metrnl levels were elevated in supernatants from BMM when compared to GM-BMM (*P < 0.0001). Culturing BMM in the presence of IL-4 led to an increase of Metrnl production whereas IFNγ suppressed Metrnl production (**P < 0.02).
Each experiment was done in triplicate and performed three times. A representative experiment (out of three) is shown.
