Figure 2.
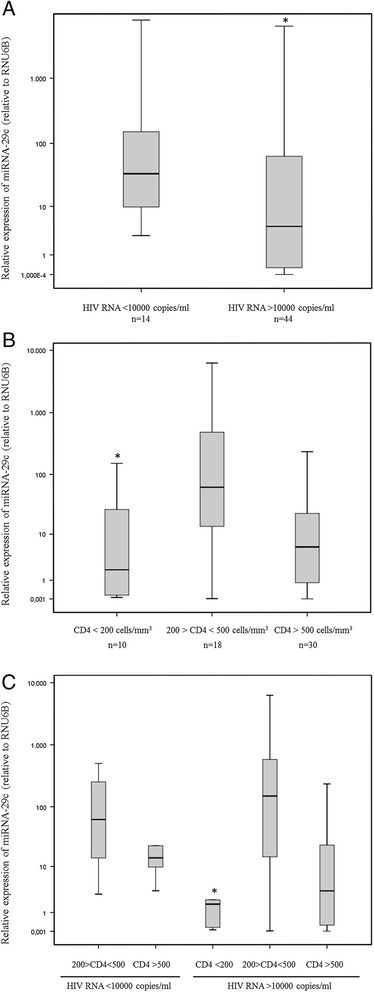
Influence of miRNA-29c levels on viro-immunological markers of disease progression in HIV-1-infected patients (n = 58) naïve for antiretroviral therapy. Panel A: miRNA-29c levels were compared in HIV-1 positive patients divided into two classes on the basis of their viral load (class I: HIV RNA >10000 copies/ml; class II: HIV RNA <10000 copies/ml). Data were analysed using the Mann–Whitney test (p = 0.038). Panel B: miRNA-29c levels were compared in HIV-1 positive patients divided into three groups on the basis of their CD4+ T cell count (low: <200 CD4+ T cells/mm3; intermediate: 200–500; CD4+ T cells/mm3; high: >500 CD4+ T cells/mm3). Data were analysed using the Kruskal-Wallis test (p = 0.019). Panel C: miRNA-29c levels were compared in HIV-1 positive patients divided into five groups on the basis of their viral load and CD4+ T cell count (Table 2). Data were analysed using the Kruskal-Wallis test (p = 0.019).
