Figure 3.
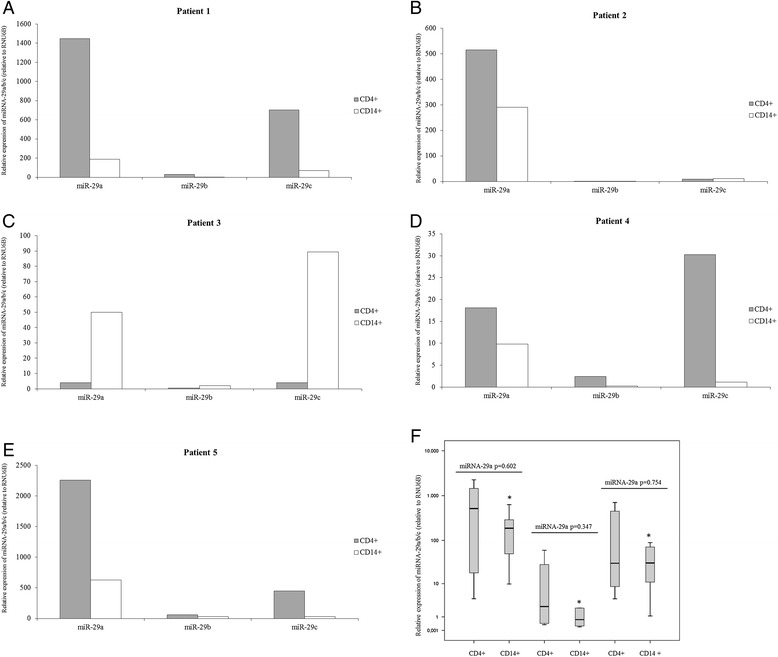
Expression of miRNA-29a/b/c in CD14+ monocytes and CD4+ T lymphocytes collected from treated HIV-1-infected patients with detectable viremia (n = 5). miRNA-29a/b/c levels were analysed in CD14+ monocytes and CD4+ T lymphocytes using real time RT-PCR assays. Panel A-E. Patient 1: viral load = 146 HIV RNA copies/ml; CD4+ T cell count = 450 cells/mm3. Patient 2: viral load = 80 HIV RNA copies/ml; CD4+ T cell count = 350 cells/mm3. Patient 3: viral load = 3278 HIV RNA copies/ml; CD4+ T cell count = 340 cells/mm3. Patient 4: viral load = 123,200 HIV RNA copies/ml; CD4+ T cell count = 400 cells/mm3. Patient 5: viral load = 1446 HIV RNA copies/ml; CD4+ T cell count = 895 cells/mm3. Panel F. Differences between CD14+ monocytes and CD4+ T lymphocytes in terms of miRNA-29 levels collected from treated HIV-1-infected patients were analysed using the Mann–Whitney test (CD4+ T lymphocytes vs CD14+ monocytes: miRNA-29a, p = 0.602; miRNA-29b, p = 0.347; miRNA-29c, p = 0.754). Kruskal-Wallis test was used to evaluate differences in expression among miRNA-29a/b/c in HIV-1-infected individuals and healthy subjects (CD4+ T lymphocytes: p = 0.114; *CD14+ monocytes: p = 0.021).
