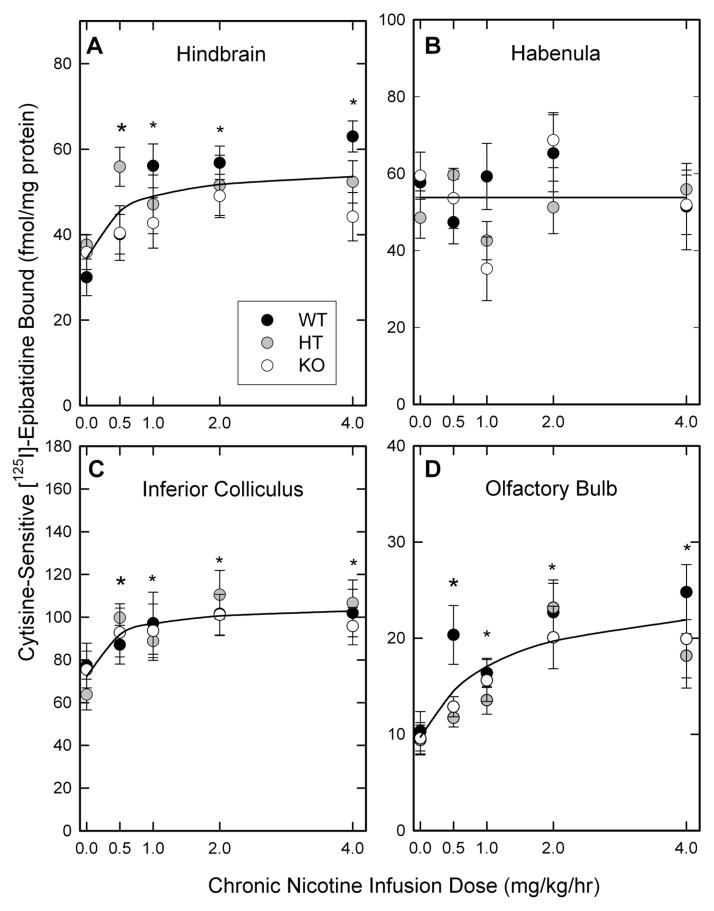
Figure 3. Effects of chronic nicotine treatment on expression of cytisine-sensitive [125I]-epibatidine binding sites.
The expression of cytisine-sensitive[125I]-epibatidine binding sites in membranes prepared from four brain regions of β4++, β4+− and β4−− mice treated with the indicated chronic doses of nicotine was calculated as described in the methods. Points represent the mean ± SEM of 5-11 independent samples. The lines in each panel are nonlinear least squares curve fits of the data. Cytisine-sensitive[125I]-epibatidine binding in each brain region except habenula was significantly higher than that of saline treated mice after nicotine treatment as indicated by the asterisks (*).