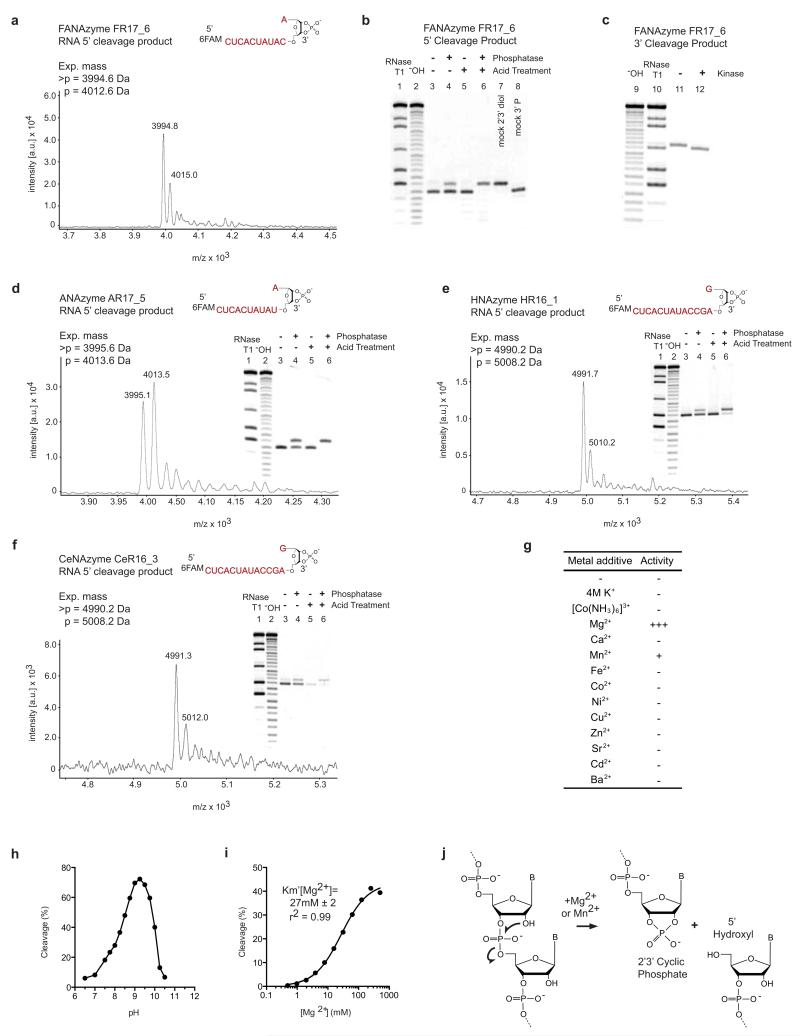
Extended Data Figure 4. Analysis of RNA endonuclease XNAzyme cleavage products.
a, 5′ cleavage product of FANAzyme FR17_6 reaction shows expected mass for a 2′,3′ cyclic phosphate (>p) using Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time of Flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-ToF). b, Hydrolysis of 5′ FR17_6 cleavage product >p in low pH and dephosphosphorylation with calf intestinal phosphatase (removes 2′p or 3′p, but not >p). c, Phosphorylation of 3′ FR17_6 cleavage product with T4 polynucleotide kinase (adds 5′p). Mass spectra and dephosphorylation assays of 5′ cleavage products of d, ANAzyme AR17_5, e, HNAzyme HR16_1 and f, CeNAzyme CeR16_3 reveal all RNA endonuclease XNAzymes yield products with 2′,3′ cyclic phosphates. (RNase T1) and (−OH) indicate partial hydrolysis reactions of the RNA substrates used. g, Bivalent metal ion requirements and titration of, h, pH or i, MgCl2, of FANAzyme FR17_6min reaction with NucSR_min. j, Reaction catalyzed by RNA endonuclease XNAzymes.