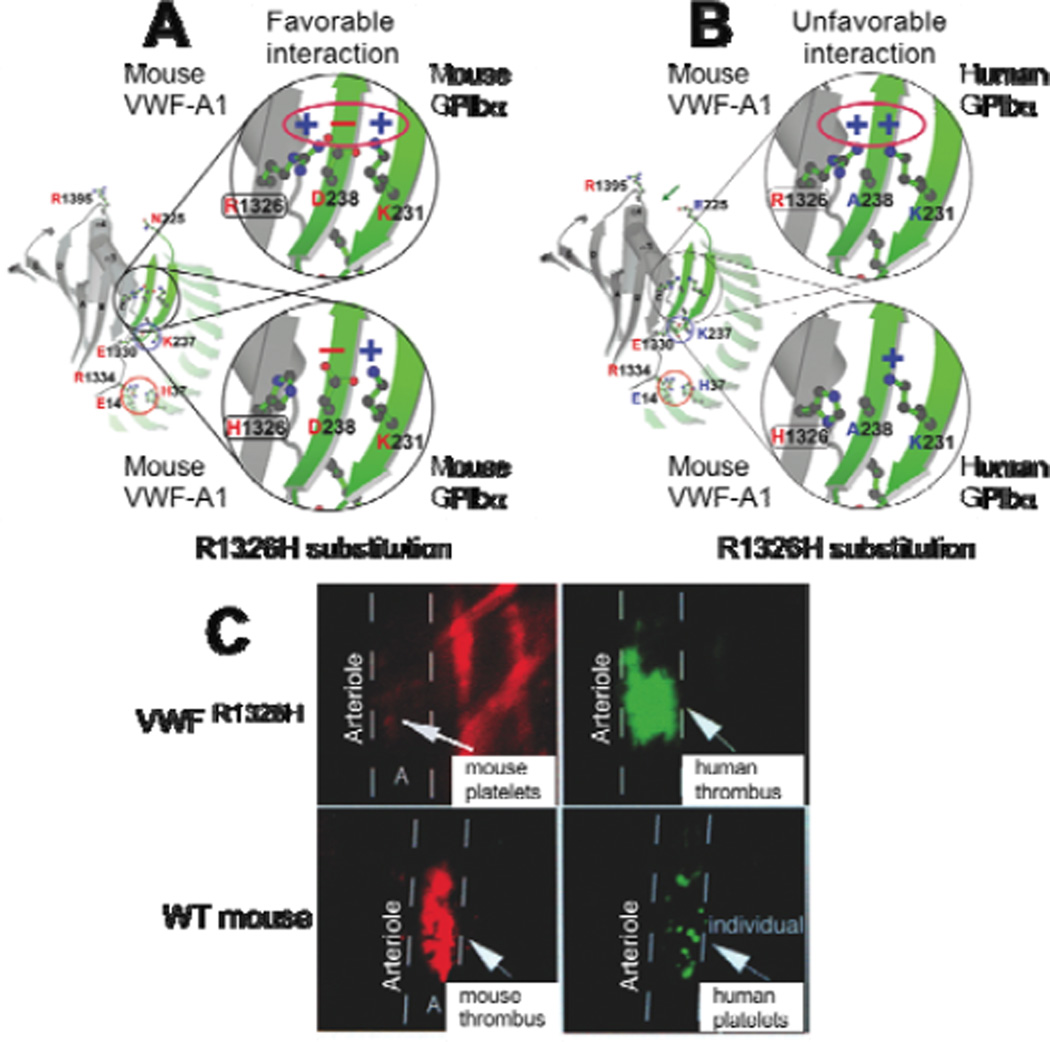
Figure 2. Effect of the arginine (R) to histidine (H) substitution in mouse VWF –A1 on the human and mouse GPIbα binding interface.
(A) Model of the mouse GPIbα–mouse VWF-A1 complex in its native state (upper panel) or with the R1326H mutation (lower panel). In the latter case, the amino acid substitution results in a loss of a favourable electrostatic interaction that supports contact between this receptor-ligand pair. (B) Model of the human GPIbα–mouse VWF-A1 interspecies complex in the absence (upper panel) and presence of (lower panel) the R1326H mutation. In the former case, there is an unfavorable electrostatic environment that would impair this interaction; the R1326H substitution prevents this from occurring and now closely resembles the human-human complex. (C) Representative photomicrographs of fluorescent images depicting mouse versus human platelet-mediated thrombus formation in VWF R1326H mutant (upper panels) or wild type (WT) mice (lower panels). Mouse platelets were labeled with rhodamine (red) and human platelets with carboxyfluorescein (green).