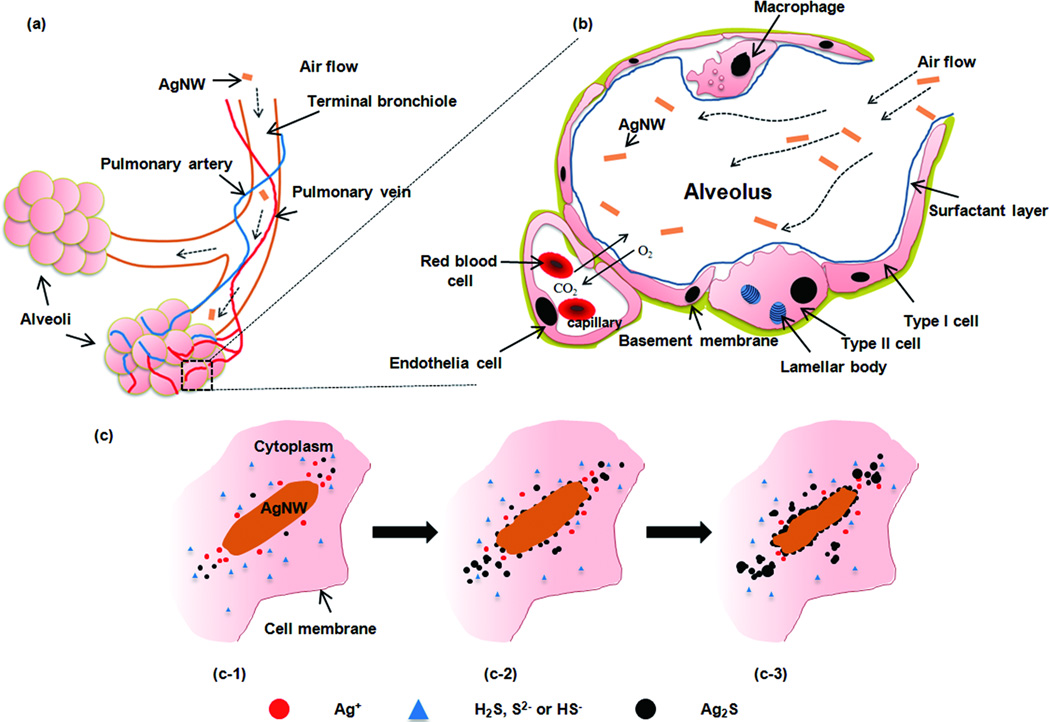
Figure 5.
(a) A schematic drawing of inhaled particles depositing into the pulmonary alveolar region, comprising the respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts and alveoli. Abundant pulmonary capillaries run through the alveoli to allow air-blood exchange. (b) A diagram of the cross section of one of the alveolus in the boxed area (a). The alveolar epithelium consists of type I, type II epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages, which are covered with a surfactant layer produced by type II cells. Gas exchange takes place at the epithelial-endothelial gas-blood barrier consisting of a mixed monolayer of type I and type II cells which share a basement membrane with the underlying capillary endothelium. (c) A schematic representation of the proposed sulfidation mechanism over time of AgNW inside type I epithelial cell.