Figure 2.
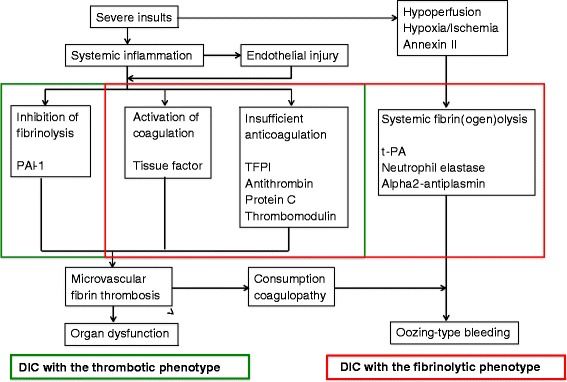
The two phenotypes of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Although the activation of the tissue factor-dependent pathway as the initial step of the coagulation cascade and the presence of insufficient anticoagulation systems are the same, DIC can be subdivided into the fibrinolytic (hemorrhagic) and antifibrinolytic (thrombotic) phenotypes. In DIC with the fibrinolytic phenotype, DIC and systemic fibrin(ogen)olysis coexist. Annexin II expression on the promyelocytes increases the tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) activity in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia. PAI-1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; TFPI, tissue factor pathway inhibitor.
