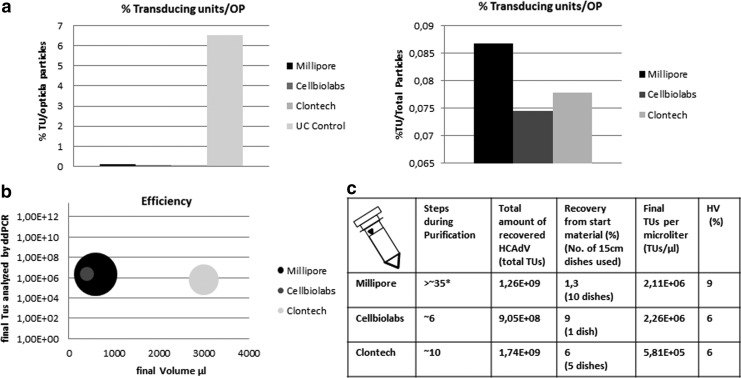
FIG. 5.
Column purification and kit performance. (a) Percentage of infectious units of HCAdV contained in final vector preparations compared with total optical particle (OP) numbers. As expected, the ultracentrifuge separates HCAdV lacking a genome from the fully assembled particles, resulting in the highest ratio of infectious units compared with optical particle numbers. The left panel shows all vector preparations, including ultracentrifugation (Uc Control), and the right panel displays only column-based purification procedures. (b) Efficacy of the different kit systems based on cell surface area purified (size of the circle), infectious titer, and final yields. In our hands, the Cellbiolabs system outperformed the other systems since it provided a significant higher amount of virus based on a small amount of starting material. On the basis of quantification of TUs, the systems provided a similar quality of purified virus. (c) Summary and comparison of the different column-based purification systems. The total number of required steps from freezing and thawing the cellular lysate to the final vector preparation is provided. In addition, the total yields of HCAdV expressed as total TUs after the purification procedure for all systems are shown. The third column summarizes the recovery rate of HCAdV from the given amount of starting material expressed as recommended amount of tissue culture dishes that were used for purification. Moreover, the final number of TUs of the HCAdV for each system per microliter and the percentage of HV contamination levels in final vector preparations are summarized for each system. For the vector purified by CsCl gradients, the HV contamination was 2.5%. *The Millipore purification system includes most steps because it makes use of a complex purification device that requires a great number of smaller steps.