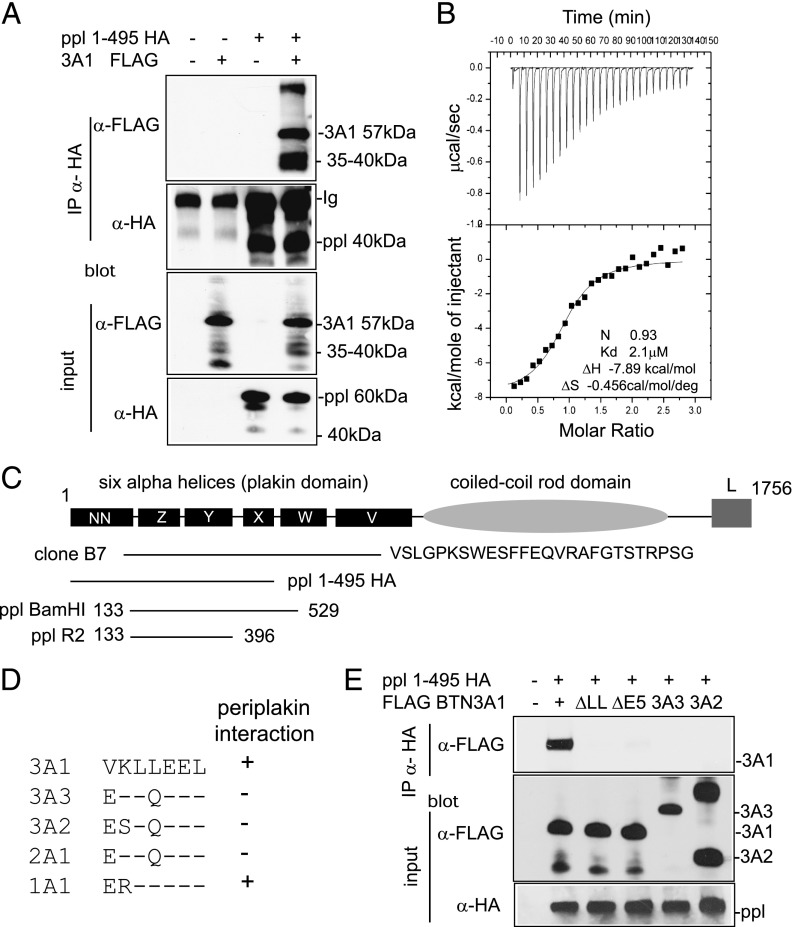
FIGURE 2.
Interaction of BTN3A1 with periplakin. (A) Interaction of periplakin and BTN3A1 in vivo by IP. 293T cells were transfected with expression constructs PPL1-495 HA and FLAG BTN3A1 either alone or together. Protein complexes were recovered by IP using anti-HA Ab and analyzed by IB using anti-FLAG (upper panel) or anti-HA (second panel) Abs. FLAG BTN3A1 was recovered from anti-HA IP only in the presence of PPL1-495 HA. Lower panels show input lysates analyzed by IB. Protein bands with molecular weights lower than the introduced expression constructs were detected for both BTN3A1 and periplakin in IP experiments, as shown, which likely represents postlysis proteolytic cleavage of proteins. (B) ITC was used to confirm thermodynamically favorable interaction between purified BTN3A1 and PPL BamH1. Binding affinity in the low-micromolar range (2.1 μM) was calculated. (C) Diagram of domain structure of periplakin (14) showing expression constructs used. Clone B7 represented periplakin aa 126–657 plus 26 additional amino acids, showing similarity to XP_001098863 periplakin-like sequence from Macaca mulatta. (D) Alignment of amino acids (306–312) encoded by exon 5 of BTN3A1 compared with other BTN proteins. (E) Periplakin interaction via the di-leucine motif in BTN3A1. IP of wild-type BTN3A1 and variants lacking either exon 5 or the di-leucine motif. 293T cells were transfected with the indicated BTN3A expression constructs together with PPL1-495 HA. Periplakin and associated proteins were recovered from cell lysates by IP using anti-HA Ab and analyzed by IB using anti-FLAG. Bottom panels show IB of input lysates using anti-FLAG and anti-HA acting as a loading control.