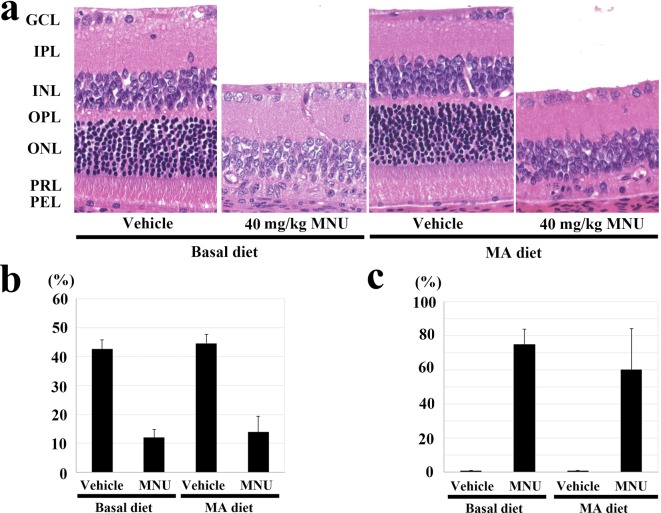
Fig. 4.
Effect of the mead acid (MA) diet on 40 mg/kg N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU)-induced retinal damage in adult rats in experiment 3. (a) Histology of the central retina in rats with or without MNU who were fed the 2.4% MA and basal diets. At 7 days after a single ip injection of MNU, the outer nuclear layer and photoreceptor layer disappeared in the rats fed the MA and basal diets. GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; PRL, photoreceptor cell layer; and PEL, pigment epithelial cell layer. HE staining, ×200. (b) Photoreceptor cell ratio in the central retina 7 days after a single ip injection of MNU in rats fed the 2.4% MA and basal diets. MNU-treated rats fed the MA diet have a statistically significant decrease in their photoreceptor ratio at the central retina, which is similar to that seen in the MNU-treated basal diet group. The index is calculated as [(outer retinal thickness / total retinal thickness) ×100]. (c) Retinal damage ratio in MNU-treated rats fed the 2.4% MA and basal diets. Rats fed the MA diet do not show any statistically significant changes in the retinal damage ratio, which is similar to that seen in the MNU-treated basal diet group. The index is evaluated as [(length of retina composed of less than four photoreceptor cells / whole retinal length) ×100]. The mean ± SE of the six or seven rats in each treatment group is shown.